Tracing AlphaCom data communication
From Zenitel Wiki
As from AMC version 11.5.3.1B it is possible to trace various data protocols. Both input and output data can be traced, including time stamp. This can be useful for troubleshooting.
Contents
Modify the configuration file for logging
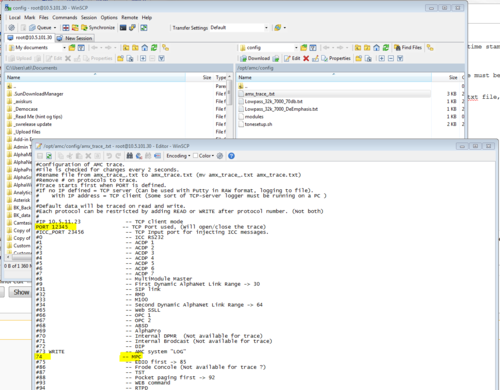
A configuration file for logging of data communication is located on the AMC-IP board, in the location /opt/amc/config/amx_trace_.txt. The configuration file is checked every 2 seconds and changes applied.
The PC program WinSCP is used to connect to the AlphaCom, open the configuration file and modify it.
In WinSCP create a New Site using:
- File protocol: SFTP
- Host name: IP address of the AlphaCom
- Port number: 22
- User name:
- Password:
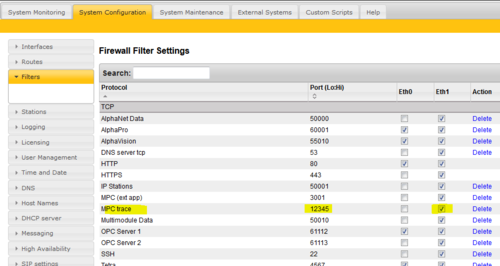
Note: Port 22 (SSH) must be enabled in the AlphaWeb in System Configuration > Filters.
Log in, and navigate to /opt/amc/config/. Open the amx_trace_.txt file by doubleclicking it, and modify the file according to the information below:
- Specify the port number to be used for the trace connection (Note that this is a different port than the external application is using for MPC data)
- Remove the "#" in front of the protocol number to be traced. (e.g. remove the "#" in front of 74 to enable MPC data trace).
- Save the file
- Rename the file from amx_trace_.txt to amx_trace.txt (I.e. remove the last "underscore").
Define the TCP port used for logging
In AlphaWeb, System Configuration -> Filters, select Add Filters and add the same TCP port as defined in the configuration file above. Remember to Enable the port, and to Apply the settings.
Collect log data
Collect the trace data from AlphaCom by using the Telnet/SSH client program PuTTY.
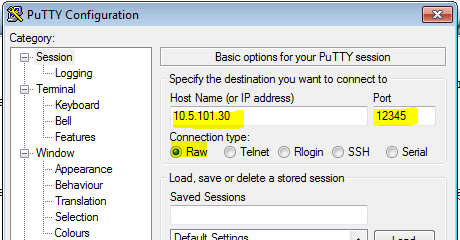
Connection setup
- Host Name: The IP Address of the AlphaCom (e.g 10.5.101.30)
- Port: The port number defined in the configuration file (e.g. 12345)
- Connection type: Raw
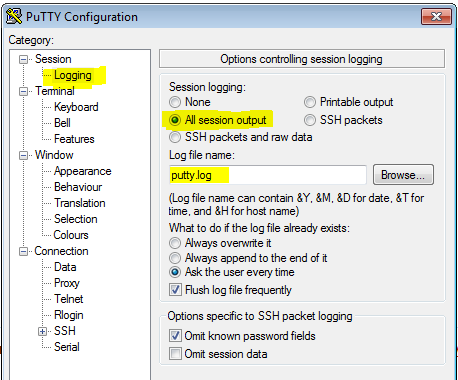
Log to file
In PuTTY select Session > Logging. Enable All session output, and choose a file name:
Now perform some activity in the AlphaCom which will generate the required data (e.g. set up a call). Open the log file, and verify that there is data in the file.
The log file for MPC data trace would look something like this:
=~=~=~=~=~=~=~=~=~=~=~= PuTTY log 2015.12.21 15:28:47 =~=~=~=~=~=~=~=~=~=~=~= 74 2 1450708072 439 13 0200 F141 74 2 1450708072 440 13 02D1 F141 74 2 1450708072 730 13 02D0 F141 74 2 1450708074 341 13 02D2 F141 74 2 1450708074 482 13 0200 F102 74 2 1450708074 483 28 0503 F141 F102 0000 0000 74 2 1450708080 65 28 0504 F141 F102 0000 0000 74 2 1450708082 854 13 0206 F102 74 2 1450708082 856 13 0201 F102 74 2 1450708082 866 13 0206 F141 74 2 1450708082 867 13 0201 F141 74 2 1450708091 368 13 0200 F102 74 2 1450708091 369 13 0200 F140 74 1 1450708091 369 13 I F102 F140 74 2 1450708091 458 28 0504 F102 F140 0000 0000 74 1 1450708101 355 8 Q F140 74 2 1450708101 651 13 0206 F102 74 2 1450708101 652 13 0201 F102 74 2 1450708101 665 13 0206 F140 74 2 1450708101 666 13 0201 F140
Data Format Description
Example log string:
74 2 1450708091 458 28 0504 F102 F140 0000 0000
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| 74 | Protocol number. 74 = MPC |
| 2 | Data From AMC (1 = read, 2 = write) |
| 1450708091 | Seconds since Epoch |
| 458 | Milliseconds |
| 28 | Number of bytes payload (one space after length not counted) |
| 0504 F102 F140 0000 0000 | Payload |