Daisy chaining of IP Stations: Difference between revisions
From Zenitel Wiki
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Daisy chain== | ==Daisy chain== | ||
[[Image:DaisyChainingOFIPstations.png|thumb|400px|Daisy chain]] | |||
The IP stations have a built-in two port switch. The ’AUX’ port can be used to connect a second IP station, and to the ’AUX’port of the second station can be connected to a third station. Up to 10 IP stations can be daisy chained in this way. | The IP stations have a built-in two port switch. The ’AUX’ port can be used to connect a second IP station, and to the ’AUX’port of the second station can be connected to a third station. Up to 10 IP stations can be daisy chained in this way. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==Loop configuration, using the spanning tree protocol== | ==Loop configuration, using the spanning tree protocol== | ||
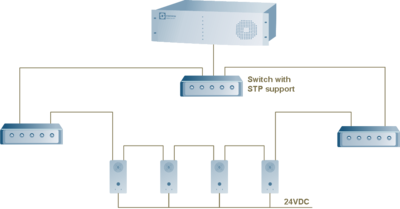
[[Image:DaisyChainingOFIPstations2.png|thumb|400px]] | [[Image:DaisyChainingOFIPstations2.png|thumb|400px|Loop configuration, using the spanning tree protocol]] | ||
*Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) is a link management protocol that provides path redundancy while preventing undesirable loops in the network. For an Ethernet network to function properly, only one active path can exist between two stations. | *Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) is a link management protocol that provides path redundancy while preventing undesirable loops in the network. For an Ethernet network to function properly, only one active path can exist between two stations. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 14:46, 5 August 2009
Daisy chain
The IP stations have a built-in two port switch. The ’AUX’ port can be used to connect a second IP station, and to the ’AUX’port of the second station can be connected to a third station. Up to 10 IP stations can be daisy chained in this way.
Daisy changing IP Stations reduces cable length
Loop configuration, using the spanning tree protocol
- Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) is a link management protocol that provides path redundancy while preventing undesirable loops in the network. For an Ethernet network to function properly, only one active path can exist between two stations.
- To provide path redundancy, STP defines a tree that spans all switches in an extended network. STP forces certain redundant data paths into a standby (blocked) state. If one network segment in the Spanning-Tree Protocol becomes unreachable, or if STP costs change, the spanning-tree algorithm reconfigures the spanning-tree topology and reestablishes the link by activating the standby path