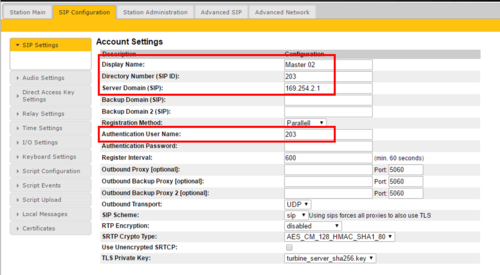
Account Settings (SIP)
From Zenitel Wiki
Contents
Main SIP account settings
On an IP Station in SIP mode, select SIP Configuration > SIP Settings to access the page for configuring the SIP Account Settings.
- Display Name: Enter a name that will be shown on the display at the remote party.
- Directory Number (SIP ID): This is the identification of the station in the SIP domain, i.e. the phone number for the station. This parameter is mandatory. Enter the SIP ID in integers according to the SIP account on the SIP domain server.
- Server Domain (SIP): The IP address of the SIP Server. This can be either an IP address in regular dot notation or a hostname.
- Backup Domain (SIP): This is the secondary (or fallback) domain. If the station loses connection to the primary SIP domain, it will switch over to the secondary one. This can be either an IP address in regular dot notation or hostname.
- Backup Domain 2 (SIP): This is the tertiary SIP domain used as backup in case the primary and secondary domains fail. This can be either an IP address in regular dot notation or hostname.
- Registration Method:
- Parallel: In Parallel mode the IP station will try to be registered to all configured SIP servers at the same time. The station will use primary SIP server for outgoing calls if available, otherwise it will use the next available backup server. In this mode the station can receive calls from multiple SIP servers at the same time. This mode is not recommended in a Cisco Unified Callmanager cluster with multiple publishers and subscribers.
- Serial: Serial registrations means that the station will always register to the next available SIP server. The station starts with registering to primary SIP server, then if the station loses contact with the primary SIP server it will register on the backup server. If the station loses contact with the backup server, then it will register on the secondary backup server. If the station loses contact with the secondary backup server it will register to the primary SIP server.
- Top-Down: Top-Down registration means that the station will try to be registered to the primary SIP server, but periodically poll the backup servers to check that they are up without registering. If primary SIP server shuts down, then the station will register to the next backup server which is up. If the primary SIP server starts up the station will unregister at the backup server and switch back to the primary server.
- Cisco: Cisco registration is the same as Top-Down for primary and backup server, while the second backup server will register to its configured server in parallell
- Authentication User Name: This is the authentication user name used to register the station to the SIP server. This is required only if the SIP server requires authentication and is normally the same as the SIP ID.
- Authentication Password: The authentication user password used to register the station to the SIP server. This is required only if the SIP server requires authentication
- Register Interval: This parameter specifies how often the station will register, and reregister in the SIP domain. This parameter will affect the time it takes to detect that a connection to a SIP domain is lost. Enter the values in number of seconds from 60 to 999999. The default interval is 600 seconds.
- Restart If Not Registered [INCA only]: If the station looses its registration towards the SIP server, the station can be forced to reboot after the preset time
- Outbound Proxy [optional]: Enter the IP address of the outbound proxy server in regular dot notation, e.g. 10.5.2.100, or as a hostname.
- Port: Enter the port number used for SIP on the outbound proxy server. The default port number is 5060.
- Outbound Backup Proxy 1&2 [optional]: Enter the IP address of the backup outbound proxy server in regular dot notation, e.g. 10.5.2.100, or as a hostname.
- Outbound transport [Turbine only]: Possible configuration options: UDP, TCP, TLS. For TCP and TLS options it is necessary to set Outbound Proxy to have the same value as Server Domain.
- SIP Scheme [Turbine only]: Possible configuration options: sip, sips. Using sips forces all proxies to also use TLS.
- RTP Encryption [Turbine only]: Possible configuration options: disabled, srtp_encryption
- SRTP Crypto Type [Turbine only]: See SIP security
- Use Unencrypted SRTCP [Turbine only]: See SIP security
- TLS Private Key [Turbine only]:See SIP security
SIP security - SIP over TLS and SRTP
Turbine has support for SIP over TLS. SIP over TLS encrypts the transport layer using the same method as HTTPS which uses certificates to validate the server. Thus the user must upload a certificate which validates the SIP server. The server can control which clients are allowed to register by using normal SIP digest authentication. TLS 1.2 is supported.
Turbine supports SRTP encryption. Current encryption formats supported are listed below:
- AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_80
- AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_32
Security Configuration
TLS
- Go to SIP Settings
- Set "outbound transport" to TLS
- Set outbound proxy address to the server address, port to 5061 (assuming standard port is used)
- Go to certificate page and upload the public certificate for the server you want to connect to. Format must be ".pem" or ".der"
- Restart main application and the station should use TLS
RTP
- Enable SRTP encryption
- Choose SRTP algorithm if default not supported
- Old Avaya servers might need to enable option for "UNENCRYPTED_SRTCP"
Asterisk server sip.conf example
sip.conf
tlsenable=yes
|
Limitations
- TCIV H264 is not supported with SRTP