Difference between revisions of "TST console"
From Zenitel Wiki
(→Data Link Trace) |
(→List Busy Resources) |
||
| (101 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{A}} | |
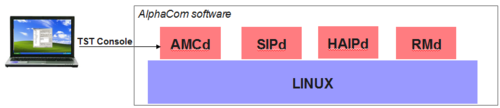
| + | [[File:TSTConsole.PNG|thumb|right|500px|The TST console]] | ||
| + | The '''TST console''' is a part of the ICX and AlphaCom Software. It is primary used as a debugging tool for software developers. | ||
| + | The TST console can be useful for troubleshooting. The TST console also gives direct access to the system memory, making it possible to modify parameters not available from the [[AlphaPro]] programming tool. | ||
| − | + | == Accessing the TST Console == | |
| − | + | The TST console is accessed from the [[Linux Console]]. | |
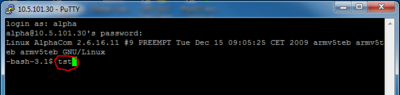
| − | + | [[File:TSTcommand.PNG|400px|thumb|right|Type "tst" at the Linux command prompt to start the TST console]] | |
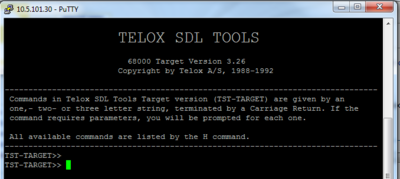
| − | + | [[File:TSTenabled.PNG|400px|thumb|right|The "TST-TARGET" prompt shows that the TST console is activated]] | |
| − | + | # Start the [[Linux Console]] | |
| − | : | + | # Depending on the system, on the Linux command prompt, type: |
| + | ## ICX System: '''tst-amcd''' | ||
| + | ## AlphaCom: '''tst''' | ||
| + | # Now the TST Console is activated | ||
| + | # Press Ctrl-C to exit the TST console and return to Linux console | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
| + | == Command Overview == | ||
| − | + | Type “xh” – to get a list of available commands. | |
| − | |||
| − | :- | + | Some commands: |
| − | + | '''nvram ''' - Edit NVRAM | |
| − | + | '''sys ''' - List Misc. System Info | |
| − | + | '''busy ''' - list busy resources | |
| − | + | '''Evh list ''' - list all Event handler events | |
| − | + | '''res ''' - List Hardware Resources by type | |
| − | + | '''nodes ''' - List all connected nodes | |
| − | + | '''stst ''' - List connected station state | |
| − | + | '''globgrp ''' - List global group node memberships | |
| − | + | '''csi ''' - Execute Command String, Simple Linklayer format | |
| − | + | '''syslog ''' - Send syslog to TST. Choose tracelevel to 7. 0 = OFF | |
| − | + | '''dno ''' - Dirno lookup | |
| − | + | '''lbus ''' - Live update of busy stations and trunks | |
| − | + | '''dt ''' - (AlphaCom) Dataprotocol Trace mode | |
| − | + | '''tstdb 4 ''' - Trace of DIP Messages between AlphaCom and IP Stations | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | === NVRAM editor === |
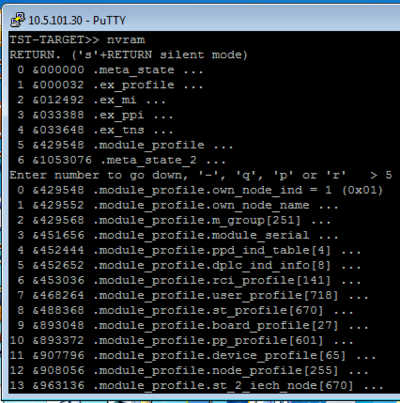
| + | [[File:TST nvram.png|right|400px|thumb|nvram editor]] | ||
| + | Command: '''nvram''' | ||
| − | + | This command can be use to inspect or modify the memory. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Note that modification will not be part of the AlphaPro database | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | '''How to use:''' | ||
| + | * On the TST prompt, type '''nvram''', then <Enter> twice | ||
| + | * You get a menu with line numbers | ||
| + | * Enter a number to select a menu line or a submenu line | ||
| + | * When a value is displayed, it can be changed by typing a new number, then <enter> | ||
| + | * Back one step: press ”-”, then <enter> | ||
| + | * Quit and save: ”q”, then <enter> | ||
| − | + | '''Text:'''<br> | |
| + | Text strings are presented as a table of byte values | ||
| + | *See the text: ”p”, then <enter> | ||
| + | *Non-pritable chars are presented as hex digits \x00 | ||
| + | *Change text: ”r”, then <enter> | ||
| + | *Use the letter ”>” before the start of text | ||
| − | + | '''How to save changes:''' | |
| + | Changes are saved to flash when leaving the NVRAM editor by pressing "q" (quit). Changes will be lost after next reset if not quiting in this way. | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
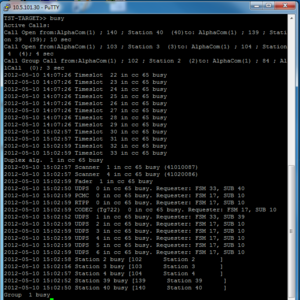
| − | + | === List Busy Resources === | |
| − | + | Command: '''busy''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | This command will list the resources currently in use in by the system. | ||
| + | [[File:TST busy.PNG|right|300px|thumb|The '''busy''' command lists currently used resources]] | ||
| − | + | Resources listed are: | |
| + | Active conversations | ||
| + | Timeslots - Backplane timeslots, of which there are 256 | ||
| + | [[Fader Resource|Faders]] - Used by the group call and simplex conference features. | ||
| + | 2 faders per ASLT, 4 faders per ATLB-12, 12 faders on the AMC-IP. | ||
| + | Scanners - Used in voice switched conversations. 2 scanners per conversation. | ||
| + | Two scanners on each ASLT/ATLB. | ||
| + | Duplex algoritms - Software resource. One (of 250) per voice switched conversation. | ||
| + | Stations - Stations currently busy | ||
| + | Group - Groups currently busy | ||
| + | UDPS - VoIP channel. Every IP device (IP station, SIP phone, AlphaNet, etc.) | ||
| + | which is sending or receiving audio is using one (of 64) VoIP channel. | ||
| + | PCMC - PCMC channels are audio links betweeen the backplane (i.e. analog | ||
| + | ASLT/ATLB users) and VoIP channels on the AMC-IP. | ||
| + | There are 32 PCMC channels. | ||
| + | CODEC - Used when transcoding between different codecs, eg. from G711 to G722. | ||
| + | Codec is also used between PCMC and RTPP, i.e. from backplane to VoIP. | ||
| + | 32 codecs available. | ||
| + | RTPP - "RTP Packetizer". Makes “Real-time Transport Protocol” packets after | ||
| + | the codec has converted PCM audio to G7xx. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
| − | == Read Error Buffer == | + | === Read Error Buffer === |
| − | + | Command: '''err''' <br> | |
| − | * | + | This command will read the content of the Error Buffer |
| + | *Internal buffer in NVRAM were special events are logged | ||
*Read out buffer to get general impression of the health of the exchange | *Read out buffer to get general impression of the health of the exchange | ||
*Find exact reason for a reset | *Find exact reason for a reset | ||
*The information is very ”software technical” | *The information is very ”software technical” | ||
*Included in the general logging facilities of AlphaCom E | *Included in the general logging facilities of AlphaCom E | ||
| − | :- Log source ”AlphaCom | + | :- Log source ”AlphaCom Debug Log” |
*Three levels: | *Three levels: | ||
:- Disaster – Exchange reset. The state of the exchange is so bad that the software does a controlled reset to restore normal operation. | :- Disaster – Exchange reset. The state of the exchange is so bad that the software does a controlled reset to restore normal operation. | ||
| Line 130: | Line 111: | ||
:- Warning – Information to the user. Often identical to texts sent to the log port | :- Warning – Information to the user. Often identical to texts sent to the log port | ||
| − | + | === Remote Login === | |
| − | == Remote Login == | ||
*”rlogin” – Remote TST Console Feature | *”rlogin” – Remote TST Console Feature | ||
:- Log on to the TST on remote node or slave modules | :- Log on to the TST on remote node or slave modules | ||
[[Image: Remote Login.jpg|left|300px|thumb]] | [[Image: Remote Login.jpg|left|300px|thumb]] | ||
| − | <br | + | <br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /> |
:- Type ”bye” to revert back to local exchange, and ”bye” once again to exit TST | :- Type ”bye” to revert back to local exchange, and ”bye” once again to exit TST | ||
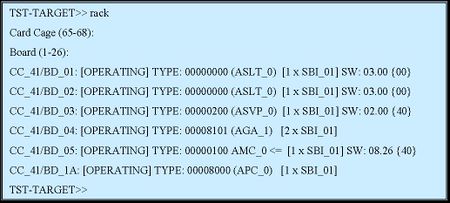
| − | == List Boards == | + | === List Boards === |
rack” – List Boards | rack” – List Boards | ||
*Gives overview of boards and hardware resources of a board | *Gives overview of boards and hardware resources of a board | ||
*Type ”rack” + <enter> + <enter> to list all boards | *Type ”rack” + <enter> + <enter> to list all boards | ||
[[Image: List Boards.jpg|left|450px|thumb]] | [[Image: List Boards.jpg|left|450px|thumb]] | ||
| + | <br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /> | ||
| + | === Data Link Trace === | ||
| − | + | "dt” – Data Link Trace | |
| − | |||
| − | dt” – Data Link Trace | ||
*Useful to debug AlphaNet or other Data Protocol problems | *Useful to debug AlphaNet or other Data Protocol problems | ||
*Activate by typing ”dt” + <enter>: | *Activate by typing ”dt” + <enter>: | ||
| − | [[Image: Data Link Trace.jpg|left| | + | [[Image: Data Link Trace.jpg|left|450px|thumb]] |
| + | <br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /> | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |"width="100pt" |To activate a continous error trace: | ||
| + | |colspan="2"|dt + <enter> + <enter> + 1 + <enter> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Turn off the trace||dt + <enter> + <enter> + <enter> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AlphaNet idle frames: ||dt + <enter> + 2 + <enter> + 2 + <enter> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AlphaNet application messages:||dt + <enter> + 1 + <enter> + 2 + <enter> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AlphaNet occational failures: ||dt + <enter> + 1 + <enter> + 1 + <enter> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | When troubleshooting an AlphaNet connection, you should first find out if AlphaNet ''data link'' is OK. You can use the dt (data trace) command to check if the AlphaNet data is ok. From the TST prompt enter dt+2+2 to start trace. Enter dt+<enter><enter><enter> to switch it off. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example 1: AlphaNet on data port 9 (IP). The ''Send'' and ''Receive'' idle frames shows that the AlphaNet data communication is OK: | ||
| + | |||
| + | DPLC(9) Recv(T1 S5 A0 L4) | ||
| + | DPLC(9) Expect(S5) | ||
| + | DPLC(9) Send(T1 S3 A0 L4) | ||
| + | DPLC(9) Recv(T2 S3 A0 L0) | ||
| + | DPLC(9) DelWin(------) | ||
| + | DPLC(9) Recv(T1 S6 A0 L4) | ||
| + | DPLC(9) Expect(S6) | ||
| + | DPLC(9) Send(T1 S4 A0 L4) | ||
| + | DPLC(9) Recv(T2 S4 A0 L0) | ||
| + | DPLC(9) DelWin(------) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example 2: AlphaNet on data port 4. The AlphaNet data communication is faulty. You can see ''Send'' but no Receive, instead there is a timer started after each Send: | ||
| + | |||
| + | DPLC(4) TIMER in READY, counter: 2 | ||
| + | DPLC(4) Send(T1 S1 A0 L4) | ||
| + | DPLC(4) TIMER in READY, counter: 3 | ||
| + | DPLC(4) Send(T1 S1 A0 L4) | ||
| + | DPLC(4) TIMER in READY, counter: 4 | ||
| + | DPLC(4) Send(T1 S1 A0 L4) | ||
| + | DPLC(4) TIMER in READY, counter: 5 | ||
| + | DPLC(4) Send(T1 S1 A0 L4) | ||
| + | DPLC(4) TIMER in READY, counter: 6 | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Data Link Statistics === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ”sswrep” – Data Link Statistics | ||
| + | *Shows quality statistics on a data link | ||
| + | *Useful if problems with AlphaNet | ||
| + | *The ”sswrep” command asks for serial port number | ||
| + | *Three counters are displayed: | ||
| + | :- P1: Total number of messages received | ||
| + | :- P2: Number of messages with wrong checksum received | ||
| + | :- P3: Number of messages received out of sequence | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image: Data Link Statistics.jpg|left|500px|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /><br /> | ||
| + | :- The counters are set to 0 when the total number of messages received reaches 50000 | ||
| + | |||
| + | === SysLog === | ||
| + | $LOG commands in the event handler and the syslog in general can be viewed in the TST console. Simply type '''''syslog''''' and select the trace level. Level 5 will only show $LOG entries, whilst level 7 will show all the syslog. (New in AMCD 11.1.3.3). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category: AlphaCom Troubleshooting]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Logging]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Upgrade and Recovery]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:09, 27 August 2019
The TST console is a part of the ICX and AlphaCom Software. It is primary used as a debugging tool for software developers.
The TST console can be useful for troubleshooting. The TST console also gives direct access to the system memory, making it possible to modify parameters not available from the AlphaPro programming tool.
Contents
Accessing the TST Console
The TST console is accessed from the Linux Console.
- Start the Linux Console
- Depending on the system, on the Linux command prompt, type:
- ICX System: tst-amcd
- AlphaCom: tst
- Now the TST Console is activated
- Press Ctrl-C to exit the TST console and return to Linux console
Command Overview
Type “xh” – to get a list of available commands.
Some commands:
nvram - Edit NVRAM sys - List Misc. System Info busy - list busy resources Evh list - list all Event handler events res - List Hardware Resources by type nodes - List all connected nodes stst - List connected station state globgrp - List global group node memberships csi - Execute Command String, Simple Linklayer format syslog - Send syslog to TST. Choose tracelevel to 7. 0 = OFF dno - Dirno lookup lbus - Live update of busy stations and trunks dt - (AlphaCom) Dataprotocol Trace mode tstdb 4 - Trace of DIP Messages between AlphaCom and IP Stations
NVRAM editor
Command: nvram
This command can be use to inspect or modify the memory.
Note that modification will not be part of the AlphaPro database
How to use:
- On the TST prompt, type nvram, then <Enter> twice
- You get a menu with line numbers
- Enter a number to select a menu line or a submenu line
- When a value is displayed, it can be changed by typing a new number, then <enter>
- Back one step: press ”-”, then <enter>
- Quit and save: ”q”, then <enter>
Text:
Text strings are presented as a table of byte values
- See the text: ”p”, then <enter>
- Non-pritable chars are presented as hex digits \x00
- Change text: ”r”, then <enter>
- Use the letter ”>” before the start of text
How to save changes:
Changes are saved to flash when leaving the NVRAM editor by pressing "q" (quit). Changes will be lost after next reset if not quiting in this way.
List Busy Resources
Command: busy
This command will list the resources currently in use in by the system.
Resources listed are:
Active conversations Timeslots - Backplane timeslots, of which there are 256 Faders - Used by the group call and simplex conference features. 2 faders per ASLT, 4 faders per ATLB-12, 12 faders on the AMC-IP. Scanners - Used in voice switched conversations. 2 scanners per conversation. Two scanners on each ASLT/ATLB. Duplex algoritms - Software resource. One (of 250) per voice switched conversation. Stations - Stations currently busy Group - Groups currently busy UDPS - VoIP channel. Every IP device (IP station, SIP phone, AlphaNet, etc.) which is sending or receiving audio is using one (of 64) VoIP channel. PCMC - PCMC channels are audio links betweeen the backplane (i.e. analog ASLT/ATLB users) and VoIP channels on the AMC-IP. There are 32 PCMC channels. CODEC - Used when transcoding between different codecs, eg. from G711 to G722. Codec is also used between PCMC and RTPP, i.e. from backplane to VoIP. 32 codecs available. RTPP - "RTP Packetizer". Makes “Real-time Transport Protocol” packets after the codec has converted PCM audio to G7xx.
Read Error Buffer
Command: err
This command will read the content of the Error Buffer
- Internal buffer in NVRAM were special events are logged
- Read out buffer to get general impression of the health of the exchange
- Find exact reason for a reset
- The information is very ”software technical”
- Included in the general logging facilities of AlphaCom E
- - Log source ”AlphaCom Debug Log”
- Three levels:
- - Disaster – Exchange reset. The state of the exchange is so bad that the software does a controlled reset to restore normal operation.
- - Error – The software handles a problem by e.g. aborting an operation and returning to idle, but logs a message
- - Warning – Information to the user. Often identical to texts sent to the log port
Remote Login
- ”rlogin” – Remote TST Console Feature
- - Log on to the TST on remote node or slave modules
- - Type ”bye” to revert back to local exchange, and ”bye” once again to exit TST
List Boards
rack” – List Boards
- Gives overview of boards and hardware resources of a board
- Type ”rack” + <enter> + <enter> to list all boards
Data Link Trace
"dt” – Data Link Trace
- Useful to debug AlphaNet or other Data Protocol problems
- Activate by typing ”dt” + <enter>:
| To activate a continous error trace: | dt + <enter> + <enter> + 1 + <enter> | |
| Turn off the trace | dt + <enter> + <enter> + <enter> | |
| AlphaNet idle frames: | dt + <enter> + 2 + <enter> + 2 + <enter> | |
| AlphaNet application messages: | dt + <enter> + 1 + <enter> + 2 + <enter> | |
| AlphaNet occational failures: | dt + <enter> + 1 + <enter> + 1 + <enter> | |
When troubleshooting an AlphaNet connection, you should first find out if AlphaNet data link is OK. You can use the dt (data trace) command to check if the AlphaNet data is ok. From the TST prompt enter dt+2+2 to start trace. Enter dt+<enter><enter><enter> to switch it off.
Example 1: AlphaNet on data port 9 (IP). The Send and Receive idle frames shows that the AlphaNet data communication is OK:
DPLC(9) Recv(T1 S5 A0 L4) DPLC(9) Expect(S5) DPLC(9) Send(T1 S3 A0 L4) DPLC(9) Recv(T2 S3 A0 L0) DPLC(9) DelWin(------) DPLC(9) Recv(T1 S6 A0 L4) DPLC(9) Expect(S6) DPLC(9) Send(T1 S4 A0 L4) DPLC(9) Recv(T2 S4 A0 L0) DPLC(9) DelWin(------)
Example 2: AlphaNet on data port 4. The AlphaNet data communication is faulty. You can see Send but no Receive, instead there is a timer started after each Send:
DPLC(4) TIMER in READY, counter: 2 DPLC(4) Send(T1 S1 A0 L4) DPLC(4) TIMER in READY, counter: 3 DPLC(4) Send(T1 S1 A0 L4) DPLC(4) TIMER in READY, counter: 4 DPLC(4) Send(T1 S1 A0 L4) DPLC(4) TIMER in READY, counter: 5 DPLC(4) Send(T1 S1 A0 L4) DPLC(4) TIMER in READY, counter: 6
Data Link Statistics
”sswrep” – Data Link Statistics
- Shows quality statistics on a data link
- Useful if problems with AlphaNet
- The ”sswrep” command asks for serial port number
- Three counters are displayed:
- - P1: Total number of messages received
- - P2: Number of messages with wrong checksum received
- - P3: Number of messages received out of sequence
- - The counters are set to 0 when the total number of messages received reaches 50000
SysLog
$LOG commands in the event handler and the syslog in general can be viewed in the TST console. Simply type syslog and select the trace level. Level 5 will only show $LOG entries, whilst level 7 will show all the syslog. (New in AMCD 11.1.3.3).