Node-Red - Getting Started
From Zenitel Wiki
Node-RED is the open-source software that is used as an event programming for Zenitel Connect Pro.
The benefits of Node-RED are
- Easy to use – Low code platform, graphical way of programming
- Although low code: still powerful
- Many existing integrations and programming examples
- Easy to re-use (export and import capability)
- Intuitive debug possibilities
For installation of Node-RED see the article: Node-Red - Installation
Contents
The Node-RED User Interface
To access the Node-RED web GUI enter https://[IP Address]:1880 in your browser, where "IP Address" is the IP address of the Zenitel Connect Pro. (e.g. "https://10.9.8.207:1880").
 |
| Node-RED User Interface |
General description
Node-RED is a graphical programming language based around receiving, processing and sending messages.
Messages can be manipulated using 'nodes' that can be dragged and dropped to the workspace, linked together in chains and then sent to the output. With respect to Zenitel Connect Pro, these messages can be events occurring in the server, such as Calls or Door Opening events. Manipulation of the message may include IF statements, setting a new parameter such as Directory Number or including a delay.
Output from Node-RED can be sent back in to ZCP to initiate a new call, or control an output or relay. It could also be towards a third party application.
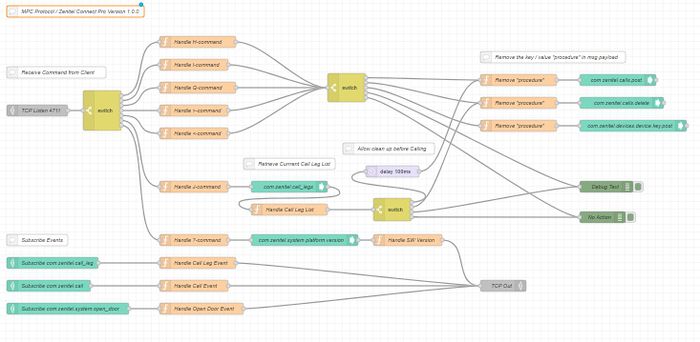 |
| Node-RED example |
Zenitel Connect Pro configuration
License
Node-RED connects to Zenitel Connect Pro as a Zenitel Link user. This requires an
- Integration license (ZCL-API) - 1002720900
Zenitel Link user
The communication between Node-Red and Zenitel Connect Pro is using the "Zenitel Link" protocol.
A Zenitel Link user must be created in Zenitel Connect Pro.
- In ZCP go to System > Users
- Press the
to add a new user
- Give the user a Name and a Password, and set the Role = "Zenitel Link User"
Firewall
The communication between Node-RED and ZCP requires that TCP port 8086 (Secure WAMP) is enabled in the firewall of the ZCP. This port is by default enabled. If you want to use unsecure WAMP, you need to enable port 8087.
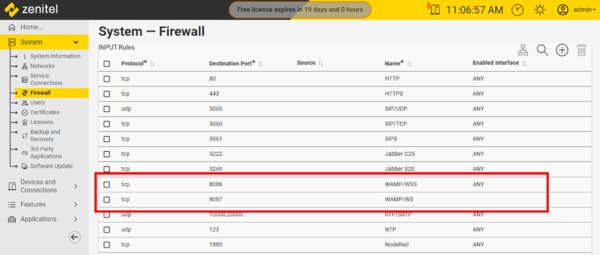 |
| Firewall ports for WAMP connection to Node-RED |
WAMP Nodes
Installing WAMP nodes
In order to connect Node-RED to Zenitel Connect Pro, the first step is to install the Zenitel specific WAMP connector nodes.
- In the Node-RED user interface click on the "Hamburger" menu icon in the top right, and choose Manage palette
- Choose the Install tab
- In the search bar, type zenitel and press enter
- Select 'Node-RED-contrib-zenitel-wamp-auth' and press Install
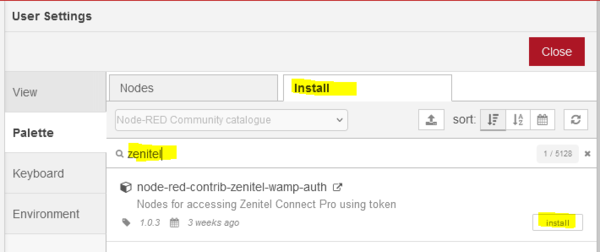 |
| Node-RED WAMP node installation |
This will install 3 new nodes available in the Palette (the left-hand side list of nodes). These three nodes are Zenitel specific: Wamp In, Wamp Out and Wamp Call.
- Wamp In is a "listener" that will subscribe to certain WAMP events in ZCP and pass these messages to other nodes in the Flow. WAMP events that the Wamp In node can connect to include items like devices and directory, groups, calls and open door.
- Wamp Out is
- Wamp Call is a "publisher" that will send messages it receives to certain WAMP connection points within ZCP. WAMP connection points that the Wamp Call node can connect to include items like calls, open door, gpos and device key emulation.
For example, to subscribe to Call events, you would drag a Wamp In node to the workspace, and subscribe to com.zenitel.calls. All call activity would be reported by this node to the next node in the chain.
To make a call using Node-RED, you would drag a Wamp Call node to the workspace, and attach it to com.zenitel.calls.post. Sending a correctly formatted message to this node would initiate a call in ZCP.
WAMP Message Formatting
ZCP sends information as an Array containing labels and values as strings. The format of these arrays varies depending on the message itself, and the format documentation is available from <zcp_ipaddress>/openapi
As an example, if we look at a Door Open event, it has the following properties
msg.payload.args[0]["door_dirno"] msg.payload.args[0]["door_name"] msg.payload.args[0]["from_dirno"] msg.payload.args[0]["from_name"] msg.payload.args[0][gpo]["gpo_id"] msg.payload.args[0][gpo]["mac_address"] msg.payload.args[0][gpo]["time"]
Using this information, we can receive Door Opening events, and process this information.
from_dirno - Directory Number of operator opening door
from_name - Display name of operator opening door
door_dirno - Directory number of Door
door_name - Display name of Door
gpo
gpo_id - Id of the GPO activated
mac_address - MAC of the device hosting the GPO being activated
time - Duration in seconds for a timed relay activation.
Node-RED receives this array as a message payload, which is referred to as msg.payload
Setting up Node-RED for the first time
When setting up Node-RED for the first time, we need to add a WAMP Connection point and the authentication details.
- Drag and drop a Wamp In node to the workspace.
- Double click on the node
- Press the + icon beside the field Add new wamp-client
- wamp.placeholder.router field: Enter the ZCP IP Address and port number "wss://<IP Address>:8086"
- wamp.placeholder.realm field: Enter "zenitel"
- wamp.placeholder.authid field: The Zenitel Link username
- wamp.placeholder.password field: The Zenitel Link password
- Name: Give your Wamp Connection a friendly name
- Click Add and then Done to finalize the properties. These details will be retained in the system
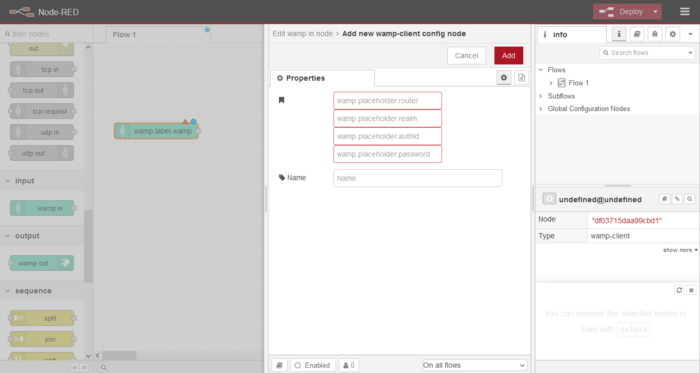 |
| Node-RED WAMP node installation |
Examples
Trigger a second Relay at Door Opening
Scenario: A client requires that in addition to the Relay being triggered at the Door intercom for access control, a second relay on another device is required to provide a signal to indicate the door has been opened. This additional signal is for a mimic panel, and for input into the Building Management System.
The directory number of the Door is 202 and the Directory number of the second device is 204.
- From the Palette, drag and drop a Wamp In node to the Workspace
- From the Palette, drag and drop a Function node to the Workspace
- From the Palette, drag and drop a Wamp Call node to the Workspace
- Connect the nodes by drawing a line between the connection points in each node
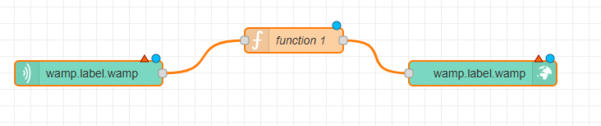 |
| Wamp In, Function and Wamp Call nodes on the Workspace |
Double-click the Wamp In node and subscribe to the Open Door event com.zenitel.system.open_door.
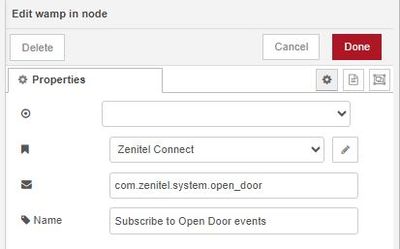 |
| The settings on the WAMP in node |
- The 1st first field is the name of the connection, which we defined in the previous step Setting up Node-RED for the first time
- The 2nd field is the event we want to subscribe to. Here "com.zenitel.system.open_door", which is the Door Open event.
- The 3rd field is any descriptive name.
The next step is to configure the Function node. Double-click the "Function" node.
Here we use a small amount of Java code within the Function node to extract the directory number from the incoming message payload and at the same time set up the new payload. The Function node extracts the value from msg.payload.args[0]["open_door"], uses an If statement to test whether the door is Dir 202, and then formats the outgoing message to be sent to the Wamp Call node.
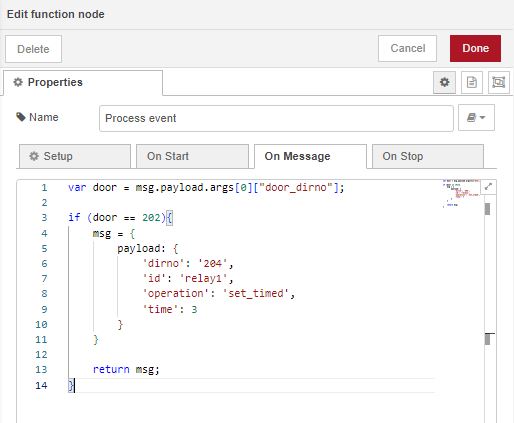 |
| The code written inside the function node |
The Function Node code is
// Retrieve the incoming number from the message payload var door = msg.payload.args[0]["door_dirno"];
// Test whether the door open is Directory number 202
if (door == 202){
// Create the new outgoing command
msg = {
payload: {
'dirno': '204',
'id': 'relay1',
'operation': 'set_timed',
'time': 3
}
}
// Send the command to the next node
return msg;
}
Finally, we can send this message to ZCP using a Wamp Call node connected to the GPO connection at com.zenitel.devices.device.gpos.gpo.post
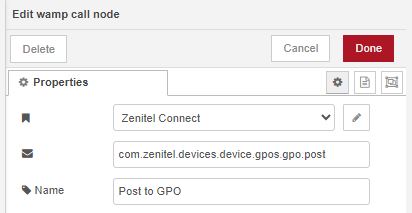 |
| The settings in the outgoing wamp call node |
Second example flow
If we have many doors in our system and we need to provide a related relay for each door, we can expand our Function node with a key-value pair table.
An IP-LCM provides up to 9 relays, so our function needs to relate to the Directory Number and the Relay to be used.
The code is
// Retrieve the incoming number from the message payload
var door = msg.payload.args[0]["door_dirno"];
// Define a lookup table for door number substitutions with an additional 'id' field
// Each door number maps to an object with 'dirno' and 'id'
var lookupTable = {
202: { dirno: 204, id: 'relay1' }, // Example: if door is 202, activate relay 1 on IP-LCM at Directory number 204
302: { dirno: 204, id: 'relay2' }, // Example: if door is 302, activate relay 2 on IP-LCM at Directory number 204
402: { dirno: 204, id: 'relay3' } // Add more pairs as needed with their respective 'dirno' and 'id'
// Add new entries here in the format: 'door_number': { dirno: 'substitute_number', id: 'relayX' }
};
// Check if the incoming 'door' number exists in the lookup table
if (lookupTable.hasOwnProperty(door)) {
// Get the corresponding object (which contains both dirno and id) from the lookup table
var substitution = lookupTable[door];
// Create a new message object with the substituted 'dirno' and 'id' values
msg = {
payload: {
'dirno': substitution.dirno.toString(), // Convert the number to string if needed
'id': substitution.id, // Use the 'id' from the lookup table
'operation': 'set_timed', // Example operation, adjust as needed
'time': 3 // Example time value, adjust as needed
}
};
// Return the modified message
return msg;
} else {
// If the 'door' number does not exist in the lookup table, return null or handle the case appropriately
node.warn("Door number " + door + " not found in lookup table.");
return null;
}
Free available data on the Internet
On the internet there are lots of API's available to request various types of data. Some of these are on a payment plan but there is also many that are provided by governments free of charge. Examples of these are weather and natural events related data or timetables for public transport. Here you can find the example of the National Weather Service in the US: https://www.weather.gov/documentation/services-web-api. In their documentation you find that https://api.weather.gov/gridpoints/{wfo}/{x},{y}/forecast gives you the weather forecast for a specific location. The values for wfo, x, and y are a location system used by the NWS, the description is in the documentation. If we fill in the values for a given location in the US we get for example a request URL that looks like this: https://api.weather.gov/gridpoints/EAX/46,52/forecast This URL can be used with the HTTP request node.
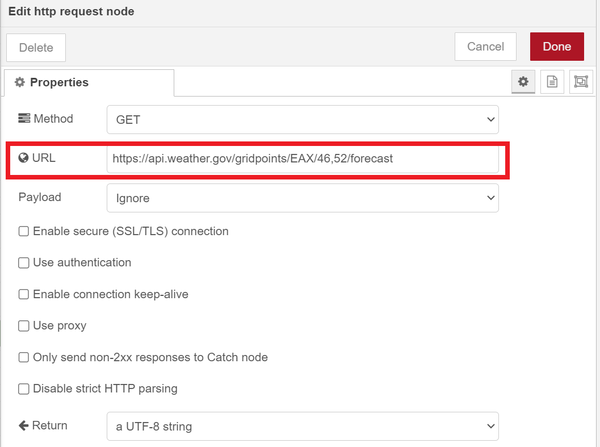 |
| The URL in the HTTP request node |
Now when this node gets triggered it will request the current weather forecast from the NWS.
Debugging and troubleshooting options
To be able to troubleshoot a flow you might want to be able to manipulate and inspect the messages being send between the nodes. There are two very useful nodes to accomplish this.
The inject node
The inject node can be used to inject a message anywhere in the flow. This can be particular useful when you are expecting a message coming from a third party system but this is not available yet. With the inject node you can start testing your flow beforehand.
 |
| The inject node |
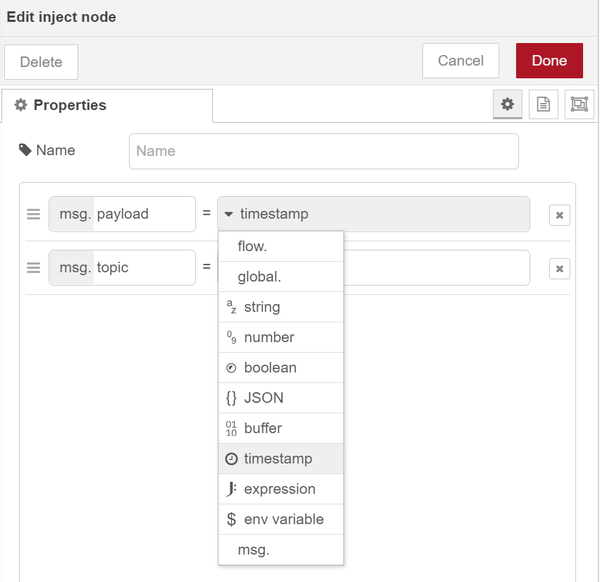 |
| The options for injecting different types of messages |
The debug node
On the right hand side of your Node-RED window there is a debug pane. You can display messages being send between nodes by using the debug node. If you have multiple debug nodes in your flow you can turn them on and off to only view the one you are interested in. In the configuration of this node you can choose to only display the message payload, which is only the actual data, or the entire message object that is including all the meta data.
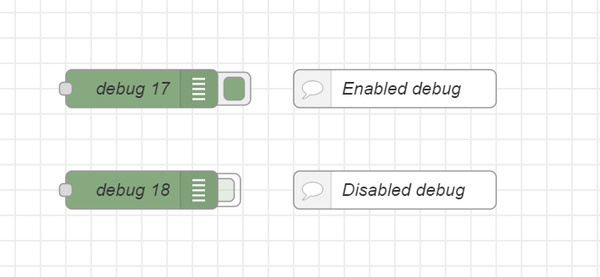 |
| The debug node |
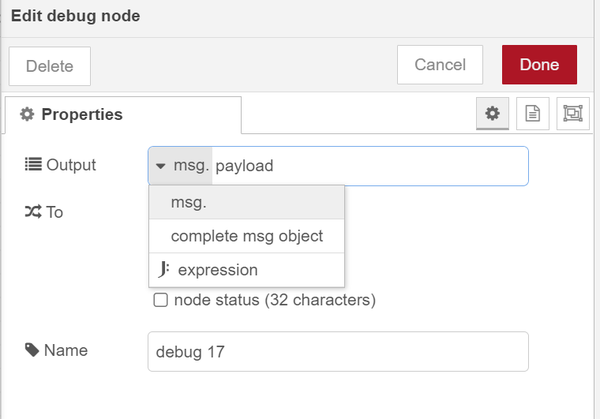 |
| The options for displaying only the payload or the entire message object |
Further reading
We advise beginners to read further in the Node-RED cookbook: https://cookbook.nodered.org

