Low Latency audio
From Zenitel Wiki
Latency refers to the delay between when an audio signal enters a system and when it emerges. Excessive audio latency has the potential to degrade call quality.
Typical scenarios where high latency might become an issue is:
- PA-Announcement where the operator hear his own announcement from nearby VoIP devices (e.g. IP Speakers or Intercoms, or PA system )
- Systems with a mix of analogue and digital audio paths. Audio from the operator is distributed partly to main PA speakers through the analogue path, and partly to speakers via a digital (VoIP) path. The analogue path will have close to zero delay, while the digital path will have some delay. Too much delay it will resulting in an echo during announcements.
A latency of 150 ms is barely perceptible and thus acceptable. However, anything over that, the quality and consistency of the call starts to decline. Latency is unacceptable at 300 ms or greater.
Reduce VoIP delay for PA-interface
When a VoIP kit is used as PA interface, one can reduce the digital signal delay by turning off all digital Voice Processing.
Log into the web interface of the VoIP kit, enable "Advanced Configuration" mode, and navigate to Audio Settings > Audio Signal Processing. Disable all processing blocks as shown below. This will reduce latency with about 60 ms.
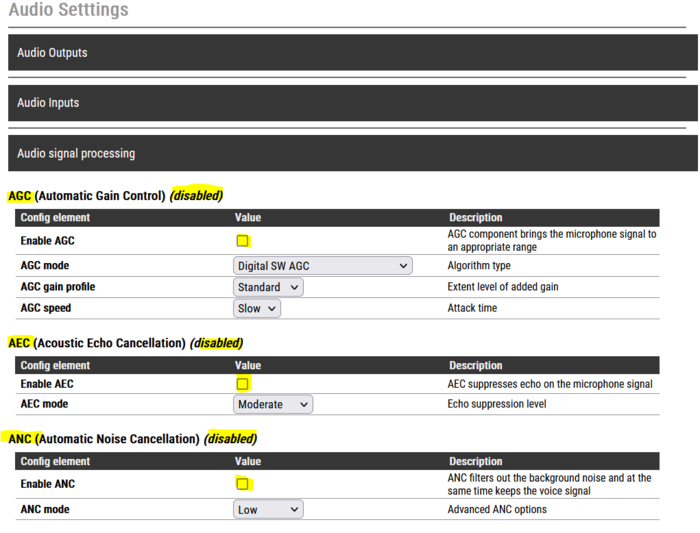 |
| Disable audio processing features |
Latency can be reduced further more by disabling “RTSP and ONVIF” on both the sender and the receiver end (when not being an ONVIF enabled system). This will reduce end-to-end delay with 20-30 ms more.
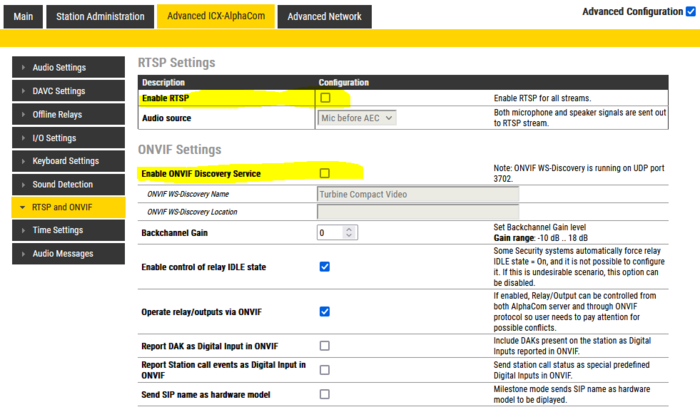 |
| Disable RTSP and ONVIF |
Also some improved receive Jitter Buffer handling should ensure lower latency.
In total end-to-end latency should be down to 50-60 ms with all measures above active.
