Difference between revisions of "MultiModule"
From Zenitel Wiki
(New page: Enter information about MultiModule here... Category:MultiModule) |
ZenitelAus (talk | contribs) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| (131 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Enter | + | {{A}}[[Image:MultiModuleXE.png|thumb|right|MultiModule: Up to 4 modules, 552 subscribers]] |
| + | The AlphaCom XE '''MultiModule''' function makes it possible to increase the capacity of '''analog station lines''' by adding up to four AlphaCom XE exchange cabinets together in a master-slave configuration. The multi-module exchange acts as one node with full integration of all features. In some documents multi-module is referred to as InterCardCage, ICC. | ||
| + | |||
| + | All configuration data are stored on the [[AMC-IP|AMC-IP board]] in the master [[module]]. The master module controls the resources in the slave modules using the [[ICC Protocol]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===MultiModule or AlphaNet?=== | ||
| + | In general MultiModule is recommended when the modules are located in the same room, and the purpose with the additional modules is to extend the line capacity. A MultiModule system being a part of an AlphaNet is seen as a single node. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[AlphaNet]] is recommended when modules are located apart from each other, in different floors, building or cities. In AlphaNet each module is a stand-alone exchange. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Licensing=== | ||
| + | When modules are connected over IP, a software license is required. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Available MultiModule licenses: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *1009640202: Multi-Module VoIP license - 2 Modules | ||
| + | *1009640203: Multi-Module VoIP license - 3 Modules | ||
| + | *1009640204: Multi-Module VoIP license - 4 Modules | ||
| + | *1009640211: Multi-Module VoIP license, upgrade + 1 module | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Note| | ||
| + | * ''The '''MultiModule license''' is required in the master module only, the slave modules do not need any license.'' | ||
| + | * ''When interconnecting modules using [[AGA|AGA boards]] or [[AE1|AE1 boards]], no license is required.'' | ||
| + | * ''Originally the '''[[Licenses#AlphaNet_license|AlphaNet license]]''' was used also for MultiModule. Although this license can still be used, it is recommended to use the MultiModule license. When using AlphaNet license, you need a license in all modules (also in the Slave modules).'' }}<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Autonom mode=== | ||
| + | The multi-module exchange supports redundancy mode. In case of master-slave communication error, the slave module will fallback to work as an individual exchange serving calls between stations connected directly to the exchange module. The AMC Master can be set to copy its content to the slave modules over a 28 hour period. In AlphaPro, '''Exchange & System''' > '''System''' > '''Calls & Options''', set the flag "Autonom Mode: Copy NVRAM". | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Audio Program feed in master=== | ||
| + | As from software AMC 10.22 and AlphaPro 10.27 there is an option to use a single audio source for program distribution in a MultiModule system, connected to the master module. See [[New_fields_%28AlphaPro_10.27%29#Groupcalls.2C_Audio_programs_to_IP_stations|Audio Program feed in master]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Module interconnections== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===IP network - VoIP=== | ||
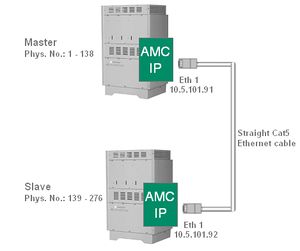
| + | [[Image:MultiModule2.jpg|left|thumb|Connecting master and slave]] | ||
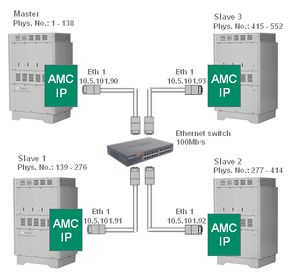
| + | [[Image:MultiModule3.jpg|right|thumb|right|An ethernet switch is needed to connect the 3 slaves and the master]] | ||
| + | When using MultiModule over IP no additional AlphaCom hardware required. Instead a license is required. There are two options:<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :- A [[Licenses#Multi_module_license|MultiModule license]]. Required in the Master module only. <br> | ||
| + | :- A [[Licenses#MultiModule_and_AlphaNet_license|channel based MultiModule license]]. Required in each module. <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Conversations between modules are point to point, and not in a ring as in traditional MultiModule using [[AGA]] or [[AE1]] boards. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The modules should be on the same LAN, as MultiModule uses fixed jitter buffer size of 10 ms | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Cabling==== | ||
| + | The modules are connected via a single Ethernet cable. Two modules can be connected back to back. A straight cat5 ethernet cable can be used. With three or four modules an ethernet switch is required. | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Programming==== | ||
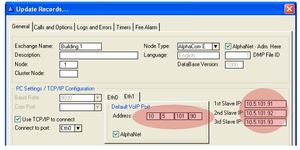
| + | [[Image:MultiModule4.jpg|thumb|right|AlphaPro: Enter the IP adress of the slave modules]] | ||
| + | Perform a [[Cold Start of AMC-IP|cold start]] of each module separately <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :'''AlphaWeb''': | ||
| + | ::- [[AlphaWeb#Ethernet_interfaces|Assign an IP Adress]] to each module | ||
| + | ::- Enable '''MultiModule Data''' (port 50010) and '''AlphaNet Audio''' (port 61000 - 61150) in the [[AlphaWeb#Filtering.2C_the_AMC-IP_firewall|Filter Setting]]. Default enabled on the Eth1 port. | ||
| + | ::- Enter the [[Licenses#Inserting_the_license_key|license key]] to enable the VoIP channels <br><br> | ||
| + | :'''AlphaPro''': | ||
| + | ::- Enter the IP adress of the slave modules. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Line switched Rings=== | ||
| + | The older AGA/AE1 based ways of inter module interconnection is still supported. Requires more HW and cabling, but provides a few advantages over VoIP makes it still an option to consider. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *less delay on voice than packed based VoIP | ||
| + | *lowspeaking call, with both handsets lifted, do not require duplex or [[Line Echo Cancellation|LEC]] resources (due to the low delay) | ||
| + | *all 30 VoIP channels can be used for AlphaNet | ||
| + | |||
| + | Even if old style using AGA/AE1 is used for inter-module audio, it is highly recommended to use TCP/IP for data-signalling to the slaves, instead of RS232. (To set up the data connection, follow same programming as in the preceding VoIP section, except there is no need for a license.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | By default AlphaCom will use AGA/AE1 rings for intermodule call as long one is available. If no (free) AGA/AE1 found, VoIP channel is used for intermodule. (Before AMCD 10.53: intermodule calls used both VoIP and AGA/AE1 channels in strict rotation). | ||
| + | |||
| + | AlphaPro flag: [[Exchange_%26_System_%28AlphaPro%29#VoIP|Exchange & System -> System -> VoIp]] "Use VoIP audio for Multi Module": Disable this flag to only use AGA or AE1 for audio distribution in MultiModule, disabling VoIP for intermodule. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====E1 link - AE1==== | ||
| + | See [[AE1#Multi-module]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====Analog links - AGA==== | ||
| + | [[Image:MultiModule1.jpg|left|thumb|MultiModule configuration using analog [[AGA]] boards]] | ||
| + | The AGA boards of the modules must be interconnected in a ring. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br style="clear:both;" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Limitations in Slave Modules= | ||
| + | |||
| + | The slave modules do not support: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Serial port drivers and other central equipment and licenses like RIO, Paging, [[AlphaNet]], SIP trunk node and SIP registrar Node | ||
| + | |||
| + | AMC versions prior to 10.43 do not support in slaves: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Remote Control Inputs - [[RCI_-_Remote_Contol_Input|RCI's]] | ||
| + | *Remote Control Outputs - [[RCO_-_Remote_Control_Output|RCO's]] | ||
[[Category:MultiModule]] | [[Category:MultiModule]] | ||
| + | [[Category: AlphaCom features]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:58, 6 August 2024
The AlphaCom XE MultiModule function makes it possible to increase the capacity of analog station lines by adding up to four AlphaCom XE exchange cabinets together in a master-slave configuration. The multi-module exchange acts as one node with full integration of all features. In some documents multi-module is referred to as InterCardCage, ICC.
All configuration data are stored on the AMC-IP board in the master module. The master module controls the resources in the slave modules using the ICC Protocol.
Contents
MultiModule or AlphaNet?
In general MultiModule is recommended when the modules are located in the same room, and the purpose with the additional modules is to extend the line capacity. A MultiModule system being a part of an AlphaNet is seen as a single node.
AlphaNet is recommended when modules are located apart from each other, in different floors, building or cities. In AlphaNet each module is a stand-alone exchange.
Licensing
When modules are connected over IP, a software license is required.
Available MultiModule licenses:
- 1009640202: Multi-Module VoIP license - 2 Modules
- 1009640203: Multi-Module VoIP license - 3 Modules
- 1009640204: Multi-Module VoIP license - 4 Modules
- 1009640211: Multi-Module VoIP license, upgrade + 1 module

|
|
Autonom mode
The multi-module exchange supports redundancy mode. In case of master-slave communication error, the slave module will fallback to work as an individual exchange serving calls between stations connected directly to the exchange module. The AMC Master can be set to copy its content to the slave modules over a 28 hour period. In AlphaPro, Exchange & System > System > Calls & Options, set the flag "Autonom Mode: Copy NVRAM".
Audio Program feed in master
As from software AMC 10.22 and AlphaPro 10.27 there is an option to use a single audio source for program distribution in a MultiModule system, connected to the master module. See Audio Program feed in master
Module interconnections
IP network - VoIP
When using MultiModule over IP no additional AlphaCom hardware required. Instead a license is required. There are two options:
- - A MultiModule license. Required in the Master module only.
- - A channel based MultiModule license. Required in each module.
Conversations between modules are point to point, and not in a ring as in traditional MultiModule using AGA or AE1 boards.
The modules should be on the same LAN, as MultiModule uses fixed jitter buffer size of 10 ms
Cabling
The modules are connected via a single Ethernet cable. Two modules can be connected back to back. A straight cat5 ethernet cable can be used. With three or four modules an ethernet switch is required.
Programming
Perform a cold start of each module separately
- AlphaWeb:
- - Assign an IP Adress to each module
- - Enable MultiModule Data (port 50010) and AlphaNet Audio (port 61000 - 61150) in the Filter Setting. Default enabled on the Eth1 port.
- - Enter the license key to enable the VoIP channels
- AlphaPro:
- - Enter the IP adress of the slave modules.
Line switched Rings
The older AGA/AE1 based ways of inter module interconnection is still supported. Requires more HW and cabling, but provides a few advantages over VoIP makes it still an option to consider.
- less delay on voice than packed based VoIP
- lowspeaking call, with both handsets lifted, do not require duplex or LEC resources (due to the low delay)
- all 30 VoIP channels can be used for AlphaNet
Even if old style using AGA/AE1 is used for inter-module audio, it is highly recommended to use TCP/IP for data-signalling to the slaves, instead of RS232. (To set up the data connection, follow same programming as in the preceding VoIP section, except there is no need for a license.)
By default AlphaCom will use AGA/AE1 rings for intermodule call as long one is available. If no (free) AGA/AE1 found, VoIP channel is used for intermodule. (Before AMCD 10.53: intermodule calls used both VoIP and AGA/AE1 channels in strict rotation).
AlphaPro flag: Exchange & System -> System -> VoIp "Use VoIP audio for Multi Module": Disable this flag to only use AGA or AE1 for audio distribution in MultiModule, disabling VoIP for intermodule.
E1 link - AE1
See AE1#Multi-module
Analog links - AGA
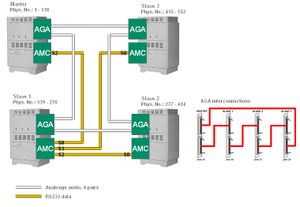
The AGA boards of the modules must be interconnected in a ring.
Limitations in Slave Modules
The slave modules do not support:
- Serial port drivers and other central equipment and licenses like RIO, Paging, AlphaNet, SIP trunk node and SIP registrar Node
AMC versions prior to 10.43 do not support in slaves: