Distributed Automatic Volume Control (DAVC) (SIP): Difference between revisions
From Zenitel Wiki
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{S|cons=}} | {{S|cons=}} | ||
[[File: | [[File:1200px-SIP_DAVC_Block_example.png|frameless|585x585px]] | ||
The '''Distributed Automatic Volume Control (DAVC)''' is an algorithm which is using one or more microphones ("AVC Source") to measure the ambient audio/noise level, and adjusts the loudspeaker output level of the PA amplifier ("AVC Receiver") according to the ambient audio level. | The '''Distributed Automatic Volume Control (DAVC)''' is an algorithm which is using one or more microphones ("AVC Source") to measure the ambient audio/noise level, and adjusts the loudspeaker output level of the PA amplifier ("AVC Receiver") according to the ambient audio level. | ||
Revision as of 15:34, 12 September 2023
 The Distributed Automatic Volume Control (DAVC) is an algorithm which is using one or more microphones ("AVC Source") to measure the ambient audio/noise level, and adjusts the loudspeaker output level of the PA amplifier ("AVC Receiver") according to the ambient audio level.
The Distributed Automatic Volume Control (DAVC) is an algorithm which is using one or more microphones ("AVC Source") to measure the ambient audio/noise level, and adjusts the loudspeaker output level of the PA amplifier ("AVC Receiver") according to the ambient audio level.
- The AVC Source is the input device with the listening microphone used for measuring the ambient noise level. This is typically an EINS-1 microphone unit, but any Turbine Device with microphone can be used. The AVC Source sends its microphone measurements to the AVC Receiver.
- The AVC Receiver is the output device that is used for playing audio, typically an ENA amplifier, or a PA Interface such as a TKIS-kit or TKIE-kit.
DAVC is not operating while audio is actively playing at the AVC Receiver. With the default configuration, it needs minimum 100ms of silence to be able to adjust the gain by 1dB. This should work just fine with normal speech, but AVC will not adjust while playing constant music.
Software requirements
- The Distributed Automatic Volume Control (DAVC) is supported as from:
- Turbine firmware v. 4.11
Configuration
AVC Source
The AVC Source is the input device with the listening microphone used for measuring the ambient noise level. This is typically an EINS-1 microphone unit, but any Turbine Device with microphone can be used.
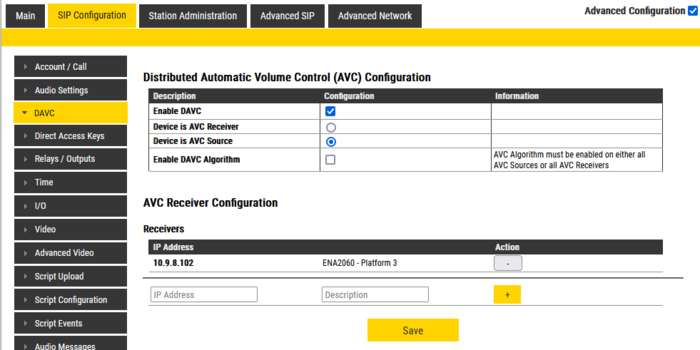
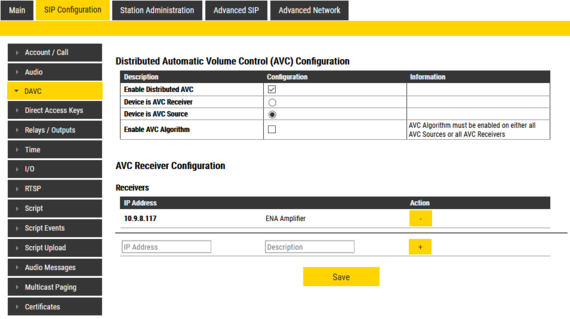
Log in to the web interface of the AVC Source, and enable Advanced Configuration. Select Sip Configuration > DAVC. Check the settings Enable DAVC and Device is AVC Source. Uncheck the other options.
Under AVC Receiver Configuration add the IP address and a descriptive name of the AVC Receiver(s):

|
Host name is not supported, only IP Address. Due to this, the AVC Receiver should have static IP address |
AVC Receiver
The AVC Receiver is the output device that is used for playing audio, typically an ENA amplifier, or a PA Interface such as a TKIS-kit or TKIE-kit.
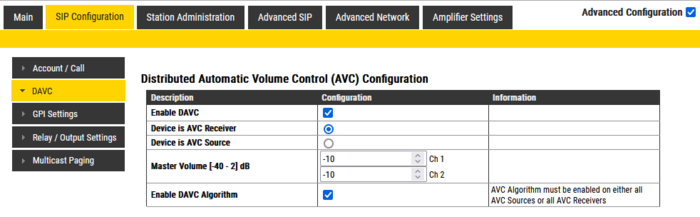
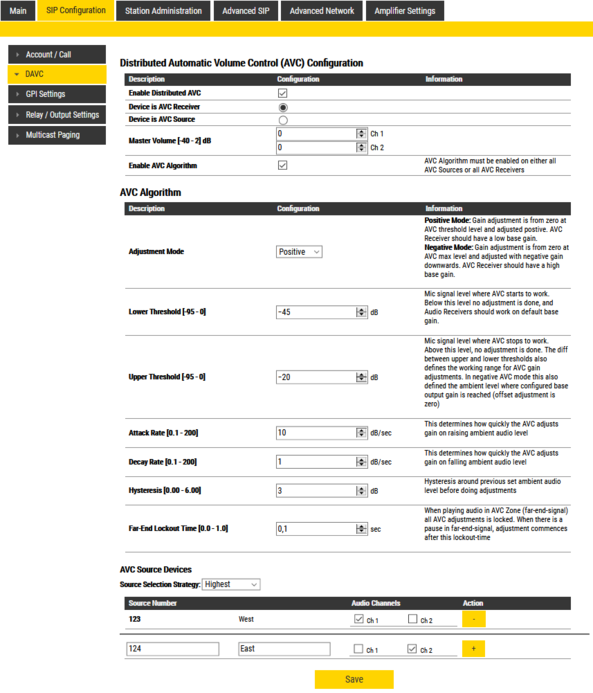
Log in to the web interface of the AVC Receiver, and enable Advanced Configuration. Select Sip Configuration > DAVC. Check the settings Enable DAVC, Device is AVC Receiver and Enable DAVC Algorithm.
If the AVC Receiver is an ENA Amplifier, the Master Volume [-40 - 2] dB sets the base gain of the two output channels. Set a low base gain when using "Positive Mode", and a high base gain when using "Negative Mode" (see below explanation).
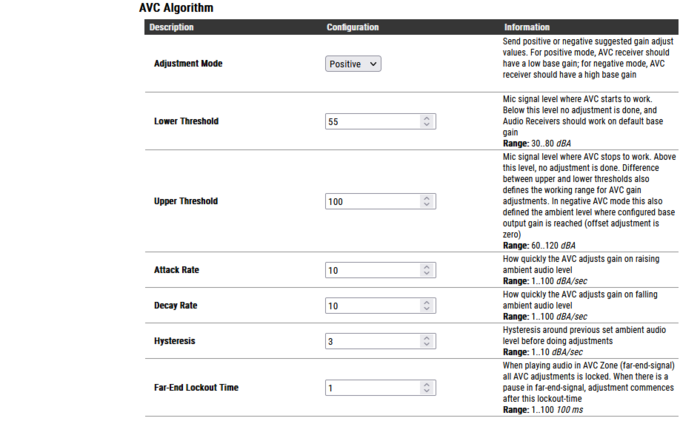
The AVC Algorithm has a set of parameters for tuning the feature:
- Adjustment Mode:
- Positive Mode: Gain adjustment is from zero at AVC threshold level and adjusted positive. AVC Receiver should have a low base gain.
- Negative Mode: Gain adjustment is from zero at AVC max level and adjusted with negative gain downwards. AVC Receiver should have a high base gain.
- Lower Threshold: Threshold level for the AVC to start working. Valid range: 30-80 dBA. Default is 55 dBA.
- Upper Threshold: Threshold level for the AVC to stop working. Valid range: 60-120 dBA. Default is 100 dBA.
- Attack Rate: How quickly the AVC adjusts gain on raising ambient audio level. Range: 1..100 dBA/sec. Default is 10 dBA/sec.
- Decay Rate: How quickly the AVC adjusts gain on falling ambient audio level. Range: 1..100 dBA/sec. Default is 10 dBA/sec.
- Hysteresis: Hysteresis around previous set ambient audio level before doing adjustments. Range: 1..10 dBA/sec. Default is 3 dBA.
- Far-End Lockout Time: When playing audio in AVC zone (far-end-signal) AVC adjustments are locked. When there is a pause in the far-end-signal, adjustment commences after this lockout-time. Range: 1..100. Resolution is 100 ms. Default is "1" (= 100 ms).
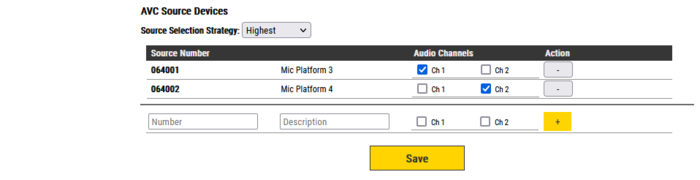
Under AVC Source Devices enter information about the remote microphone device(s):
- Source Number: The directory Number of the remote microphone device
- Audio Channels: Which audio channel(s) on this device should be effected by signals from the remote AVC Source
- Source Selection Strategy: The AVC Receiver will receive ambient audio levels or Gain adjust values from a number of AVC Sources. This configures the selection strategy for final gain adjusts on AVC Receiver.
- The different settings are: Highest, Average, Average Mid. "Average" requires two or more AVC Sources. "Average Mid" will remove high and low values if more than 4 AVC sources, and average rest.

|
If the AVC receiver is a TKIS-2 or TKIS-2 based device (e.g. IP Loudspeaker), make sure the inbuilt AVC is disabled. |
Firewall settings
On the AVC Receiver, AudioData (UDP port 5035) must be enabled in the Firewall.
Example Configuration
In this example one channel of an ENA Amplifier is used in one zone, and the other channel is used in another zone. There is one EINS-1 in each zone, measuring the ambient noise level in the zone. The EINS-1 with directory number 123 must be configured to adjust the channel 1 output of the ENA Amplifier, while the EINS-1 with directory number 124 must adjust channel 2.
ENA Amplifier configuration
The ENA Amplifier is configured to be the Audio Receiver. Adjustment Mode is set to "Negative", and the two TKIS units are configured to adjust the associated channel of the ENA Amplifier.
EINS-1 configuration
Both EINS-1 units must be configured to report ambient noise level to the ENA Amplifier at IP 10.9.8.117: