Pulse System Description
From Zenitel Wiki


|
The PULSE system is obsolete, and is replaced by the IC-EDGE System |

Overview
The Vingtor-Stentofon Pulse system is a SIP intercom system intended for small to mid-size installations for up to 64 IP stations. Some of the key features of Pulse are:
- Easy to install and configure
- Cost effective for solutions where up to 64 IP stations are needed in the network
- Supports creating Pulse trunks to inter-connect up to 50 different Pulse systems
- Single Pulse system works across multiple network subnets
- SIP Gateway interface that is easy to setup (e.g. SIP-to-GSM, SIP-to-PSTN, etc.)
- Open IP standards (SIP, HTTP(S), NTP, SNMP, RTP, etc.)
- Shared network infrastructure with other systems (CCTV, PCs, etc)
- Special SDK with API that can be used to create custom intercom solutions
- Integrated managed switch in terminals
- Wide set of special purpose IP stations and PC client
- VS-IMT: Dedicate management tool for easy configuration of large number of stations
Pulse server functions
Specifications
| Call capacity | |
| Max no Vingtor-Stentofon terminals | 64 |
| Max no 3rd party terminals | 10 |
| Max no VS-Clients | 10 |
| Max no two way calls | 32 |
| Max no group calls | 4 |
| Call setup time two way calls | 100 ms |
| Call setup time all call | 300 ms |
| Operation and maintenance | |
| Autodiscovery | Yes |
| Centralized management | Yes |
| Encrypted communication | Yes |
| Integrated web server | HTTP(S) |
| Software download | TFTP |
| Network clock | NTP |
| Multiple language | Yes |
| Admin menu | Yes |
| User menu | Yes |
| External communication | |
| Interface | Analogue/GSM |
| SIP Gateways | |
| Audiocodes MP-114 | Analogue FXO |
| Grandstream HT503 | Analogue FXO |
| Portech MV-370 | GSM |
| SIP telephones | |
| Grandstream | GXP1625, GXV3240, GXV3275 |
| SNOM | SNOM870, SNOM821 |
| Softclients | X-lite, Bria |
| Cisco | Cisco 9971 |
| Yealink | VP530, T48G, T49G |
| VoIP protocols and functions | |
| SIP support | RFC 3261 (SIP base standard) |
| RFC 3215 (SIP REFER) | |
| RFC 2976 (SIP INFO) | |
| DTMF support | RFC 2833, 2976 (SIP info) |
| SDP | RFC 4566 |
| RTP | RFC 3550 |
| Audio functions | |
| Adaptive Echo Cancellation (AEC) | Yes |
| Noise Reduction (NR) | Yes |
| Automatic Volume Control (AVC) | Yes |
| Microphone sensitivity | Configurable |
| Volume control | Yes |
| Push to talk mode | Yes |
| Open duplex (AEC) | Yes |
| Switched duplex (AES) | Yes |
| Voice codec | G.722 (HD Voice) |
| G.711 A and µ (Telephony) | |
| G.729 | |
| Jitter buffer | Adaptive |
| IP networking and security | |
| 2 port data switch | |
| Supplementary functions | |
| Call hold | Yes |
| Call transfer | Yes |
| Call forwarding | Yes |
| Group call | Yes – 4 groups and priorities |
| Ring list | Yes – parallell calling |
| Busy override | Yes |
| Remote control | Yes |
| Group Call answer | Yes |
| Group Call w/ Recall | Yes |
| Call queuing | Yes |
| Network Multi-Subnet support | Yes |
Protocols and network ports
| Protocol name | TCP / UDP | Port | Description |
| SSH | tcp | 22 | |
| TFTP Server | udp | 69 | |
| HTTP | tcp | 80 | |
| SNMP | udp | 161 | |
| HTTPS | tcp | 443 | |
| SIP | tcp | 5060 | |
| SIP | udp | 5060 | |
| SIPS | tcp | 5061 | |
| Pulse | udp | 5062 | |
| mDNS | udp | 5353 | |
| ZapWeb | tcp | 8080 | |
| DIP | tcp | 50001 | |
| DIP Multicast | udp | 50001 | |
| Discovery | udp | 50002 | |
| ZAP | tcp | 50004 | |
| Demo | tcp | 50010 | |
| VoIP | udp | 61000:61150 | VoIP port range is configurable on StationWeb. Note: only works for SIP mode |
Reserved IP addresses and ports
| Service | TCP / UDP | Address / Port | Description |
| Group Call control | UDP | 239.192.2.0 :50001 | |
| Group Call audio | UDP | 239.195.0.0/16 :61060-61066 | Server will generate a set of multicast addresses to use based on it's MAC address |
| Station Auto-discovery | UDP | 239.192.0.199 :50002 | Station auto-discovery uses both broadcast and multicast |
Dialing method
Pulse uses overlap dialing method. Overlap signaling means that digits are sent one by one from the station to the server (and not collected in the station and sent as a block, known as En Bloc dialing). Using overlap signaling, call setup can begin before all the digits have been collected.
Gateway interface and external communication
The Pulse server can be configured with up to 10 Gateway accounts. Appropriate Pulse-Server-TelTrunk license allows user to create one GSM or telephone trunk channel in a Pulse Server; the Gateways parameter will be available under Server Management -> Server Configuration -> Directory Settings. For every gateway a separate SIP Gateway account needs to be configured.
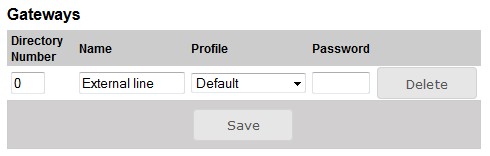
Directory Number 0 is optional as you can use any number to make external calls through the Gateway.
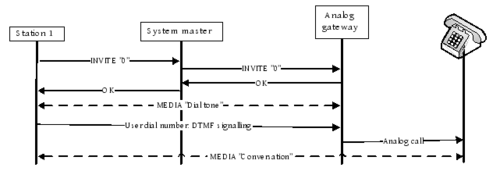
Configuring the Telephone Gateway is done by logging into the Telephone Gateway to register it to the Pulse Server by using the created SIP Gateway Account.
Currently supported Gateway devices are and their configuration is described in separate articles:
Support for 64 stations
A single Pulse system supports up to 64 registered Vingtor-Stentofon IP stations. The auto-discovery feature makes it easy to configure larger Pulse installations using only station built-in web services.
Pulse will allow for 16 IP stations to register out-of-box without any licenses. The system can be further expanded by installing an IP Station license for each additional intercom.
For more details see:
Station auto-discovery and configuration
All Vingtor-Stentofon IP stations use auto-discovery feature which enables fully automatic discovery of all the IP stations on then network by Pulse server.
Station configuration can be done directly from Pulse server StationWeb. After IP stations are discovered with Pulse station auto-discovery, they can be immediately set up and configuration saved and applied for multiple stations at once. All the basic functions can be directly configured from Pulse server. For more specific configuration and customization, StationWeb of every IP station can be used as configuration tool. In addition, VS-IMT tool can be used to configure one or multiple stations in Pulse system.
More info can be found in Station auto-discovery and Configuration (Pulse).
Multi-subnet support
Pulse can be deployed as a single-server system with IP stations being installed in different network subnets. There are some prerequisites for network setup so Pulse can operate without problems:
- Network subnets (segments) with IP stations need to be routable
- IP Multicast routing needs to be enabled and configured on the layer-3 switch or router. This is required by Pulse IP station auto-discovery and Pulse Group Call functions
- All protocols and ports that Pulse IP stations are using must not be filtered between network subnets
Network with multiple Pulse systems
In scenarios where multiple Pulse systems are installed with dedicated servers on different subnets, IT administrator should block all multicast traffic between different Pulse systems. Still, Pulse handles such scenarios in the following way:
- Group calls: Each Pulse client will receive "Pulse server ID" during registration process and it will filter out all the group calls multicast traffic if it does not belong to this "server ID". In addition, each server will generate a set of multicast audio addresses based on it's unique MAC address.
- Station Discovery: During configuration of Pulse clients on sever StationWeb, discovery of all IP station on network is done. Those stations that are configured with another server IP address will automatically be deselected for configuration.
Server Call Forwarding
The Pulse Server supports server side call forwarding. When a station activates call forwarding it will notify the Pulse Server, which will store the call forwarding state. The Pulse Server will handle call forwarding for the station, thus the call forwarding will work even if the station is off-line. Forwarding status can be observed on the web page of the Pulse Server ("Server Monitoring"), where the target station of the forwarding is shown.
Pulse Trunking
Pulse Trunking is a feature in the Pulse Server for enabling calls between different Pulse sites. The function is enabled with Pulse-Server-Enterprise license. A total of 50 trunk routes can be configured on the Pulse server.
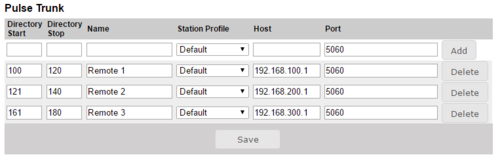
Pulse Trunk Routes must be configured to enable calls between different Pulse sites. A route consists of:
- Number range for the site the route goes to
- Logical name for the route
- IP address and SIP port of the remote Pulse Server on the remote site (Pulse Server SIP port is normally 5060)
- Profile to assign calls coming from/to the route. Profiles can be used to restrict access to/from a route
For two sites to call each other 2 routes must be configured. First, a route must be configured in Pulse Server 1, the route must define the number range of Pulse site 2 and the IP address of Pulse Server 2. In addition Pulse Server 2 must have a configured route to Pulse site 1, with the number range of Pulse site 1 and IP address of Pulse Server 1.
If only 1 route is enabled, site 1 with the Enterprise license can call site 2, but site 2 cannot call site 1
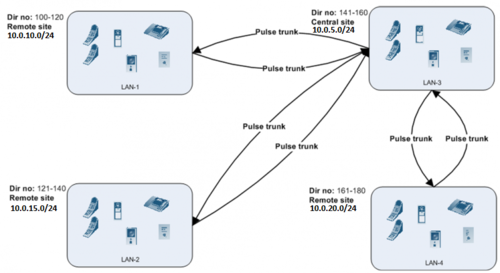
A client may only call to sites where there exists direct routes. In the example, the Remote sites may only call Central site, because only a route to Central site is configured. The Central site may call all of the Remote sites because it has routes configured to each Remote site. Configuration example for Central site Pulse server:
Pulse SDK
Pulse system can be extended and customized with VS-SDK for Pulse. Key features are:
- Build your own Vingtor-Stentofon Pulse intercom solution
- Java and .NET APIs with ready-to-use examples and documentation (Intercom API)
- Remotely control Turbine intercoms
SDK comes with easy to use API, out-of-box integration with Pulse Intercom system, support for all Turbine Intercom devices and PC soft-client, demo apps, code examples and API reference documentation. Intercom API even supports advanced Call center functions.
