AlphaNet
From Zenitel Wiki
AlphaNet is STENTOFON's internal networking technology made for critical communications. Some of the highlighted features of AlphaNet are:
- Group and conference calls
- VoIP bandwidth management
- Priority handling of events and resources
- Alternative routing
- Backwards compatibility
- All features available over the network
- VoIP, digital and analogue infrastructure support
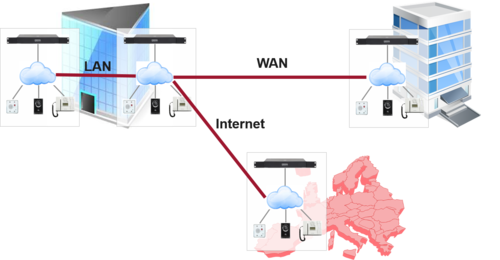
Up to 254 AlphaCom servers can be interconnected in AlphaNet. One AlphaCom server can have links to 50 other servers (100 links as from AlphaCom ver. 12.5.3.4). If there are more that 50 servers, transit routing must be used.
VoIP AlphaNet Configuration
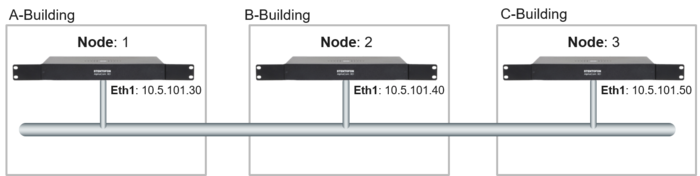
The following configuration is used in the examples in this article.
AlphaWeb settings
In each node you must:
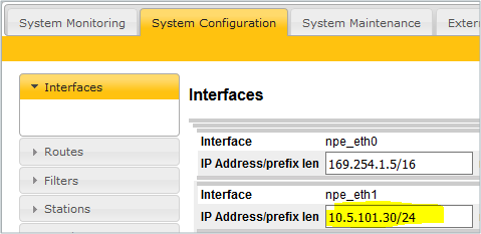
- Set a unique IP address
- Insert an AlphaNet license
- Edit the firewall
Setting IP address
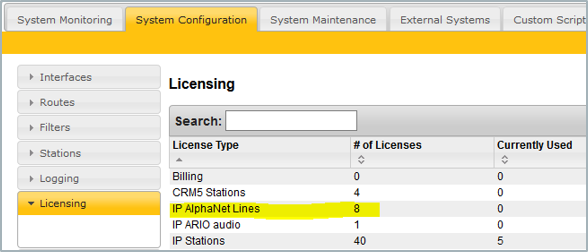
Inserting AlphaNet license
Every AlphaCom node requires an AlphaNet license. The license controls the number of simultaneous calls to and from an AlphaCom.
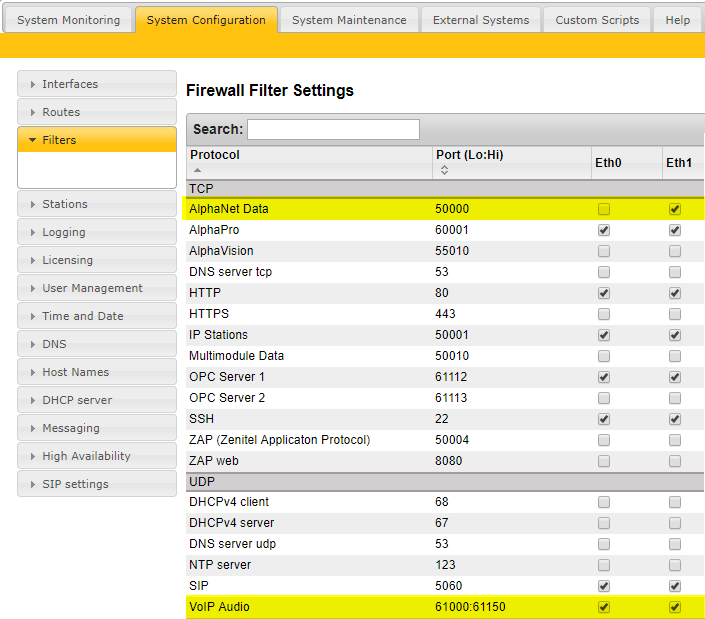
Editing the firewall
TCP port 50000 must be enabled in for signaling between the nodes, and UDP ports 61000-61150 for VoIP audio:
Create all the nodes in the AlphaNet
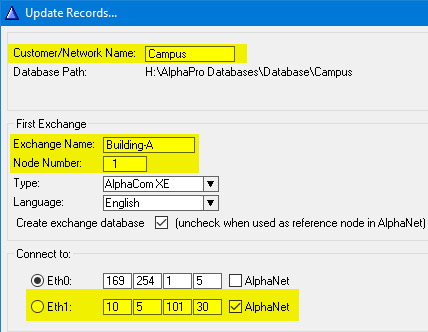
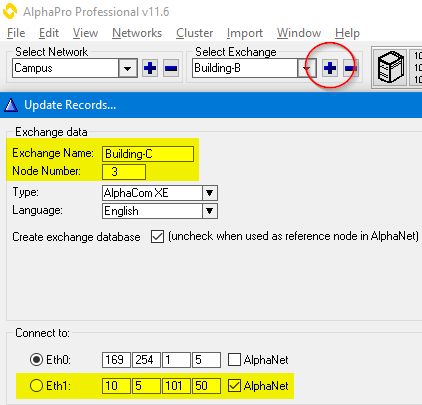
Create the AlphaNet database and define the first node by clicking the + sign as highlighted below. Give the node a descriptive name and select which network interface to be used to communicate with other nodes.
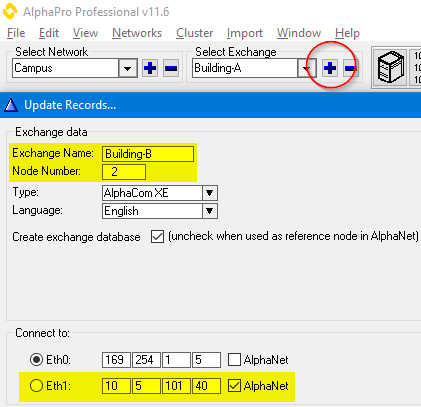
Add more nodes to the database by clicking the + sign as highlighted below. Give the node a descriptive name and select which network interface to be used to communicate with other nodes.
Create AlphaNet routing
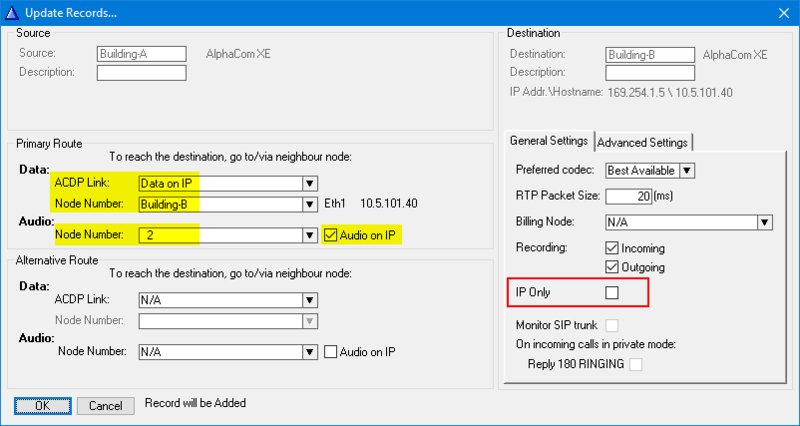
Routing must be specified from all nodes to all nodes. For each node:
- Click on Exchange & System > Net Routing > Insert
- Select the remote AlphaCom node from the list of unconfigured nodes that pops up
If the the Source Node is an AlphaCom XE7/20/26 and the Destination Node is an AlphaCom XE1, enable “IP Only”
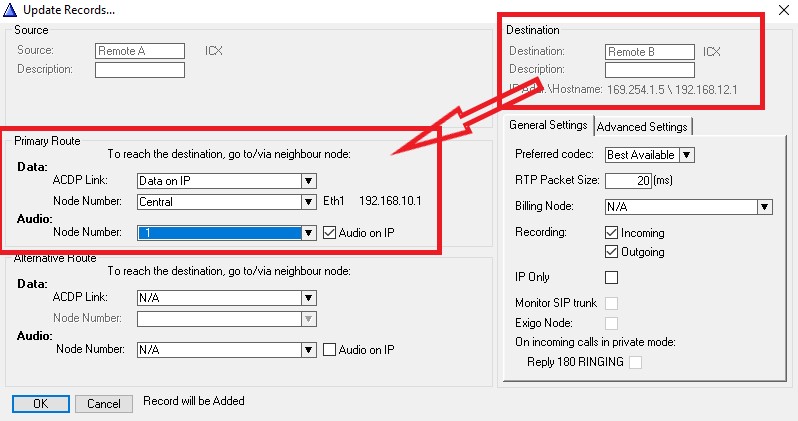
Transit Routing
In the case of Transit Routing, where the Remote nodes are connected via a Central Node, you need to direct the traffic via the Central Node.
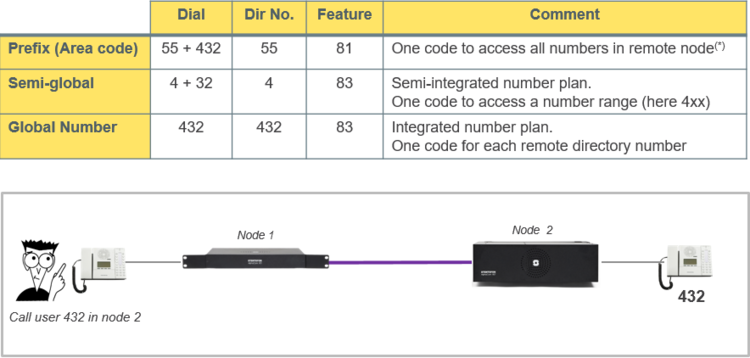
Dial plans
Calling from station A in one node to station B in another node can be achieved in different ways.
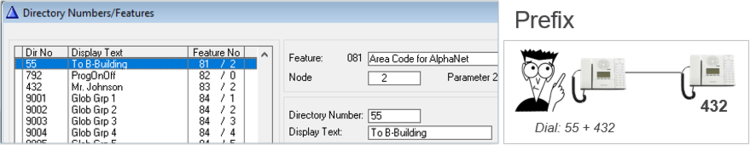
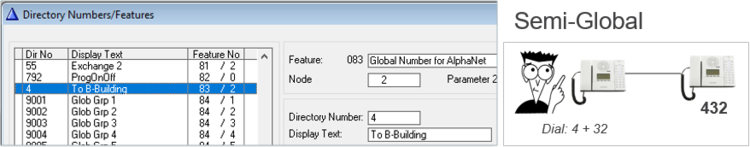
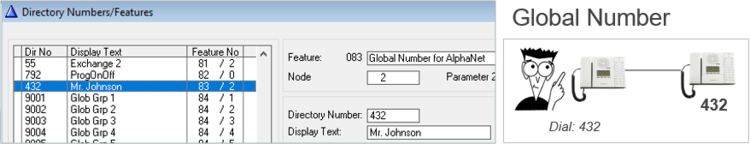
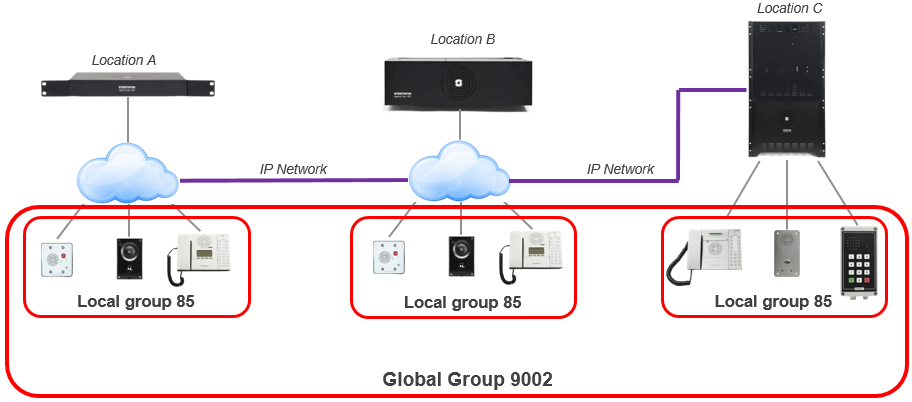
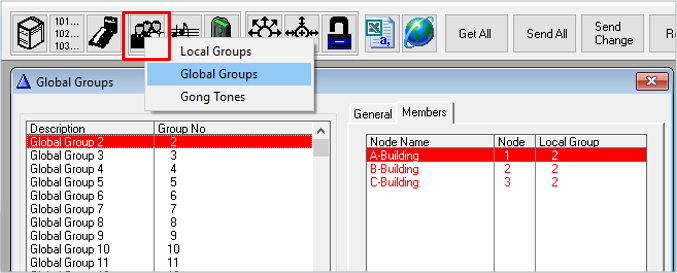
Global Group Calls
A Global Group consists of one Local Group from each node
- Factory Default includes Global Group 1 to 10, Directory Numbers 9001 – 9010
- Each Global Group can contain one local group call from each node
Each node broadcasts its own global group membership to the other nodes after:
- AlphaPro Send operation
- Restart of AlphaCom
- Dialing service code 7879
In this way each node knows which global groups the other nodes are members of.
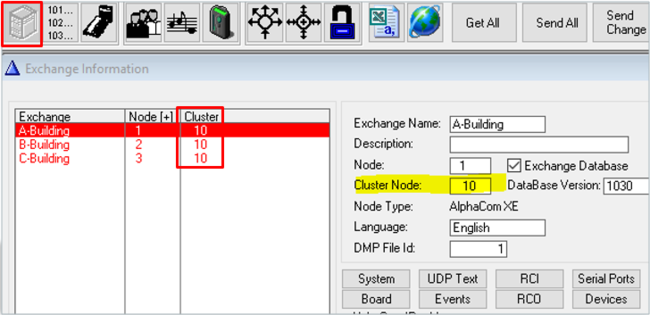
Cluster node programming
Defining Cluster Node
Cluster programming is an option to simplify programming and updating of numbers in AlphaNet when operating with integrated number series. To get access to the AlphaNet Visibility menu, the server must be assinged a Cluster Node Number in the Exchange & System window. The Cluster Node number can be any number between 1-255. Nodes with the same Cluster Node Number are members of the same cluster.
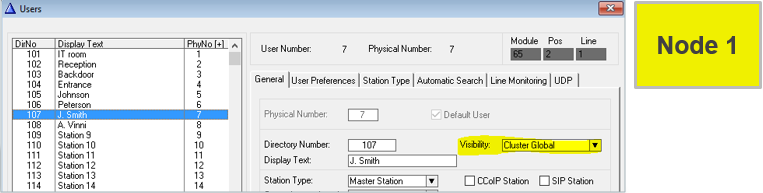
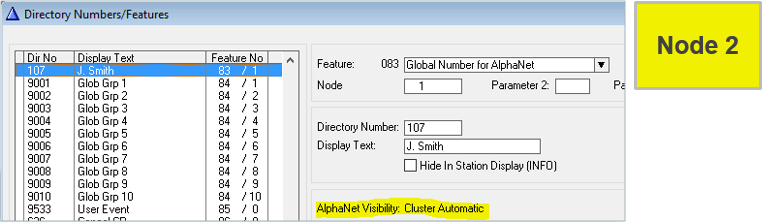
Cluster Global
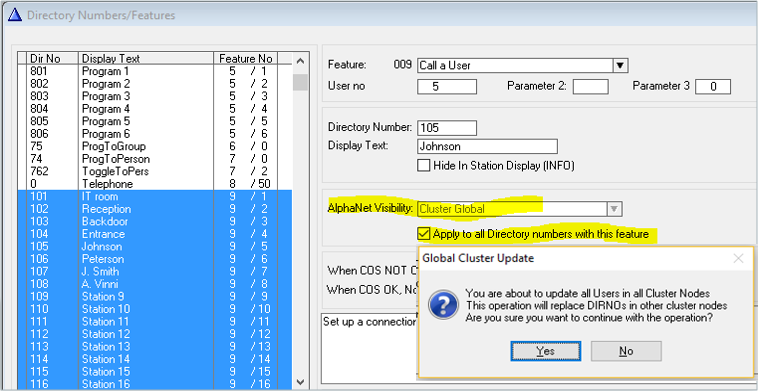
Setting Visibility = “Cluster Global” on a User in node 1...
...will automatically create a Global Number (feature 83) in node 2 (and all other nodes in the cluster)
It is possible to create Global Numbers for many (or all) Users in one operation:
- In Directory & Features select multiple users (feature 9) by click and shift + click.
- Set AlphaNet Visibility = “Cluster Global”
- Check “Apply to all Directory Numbers with this feature”
Cluster Identical
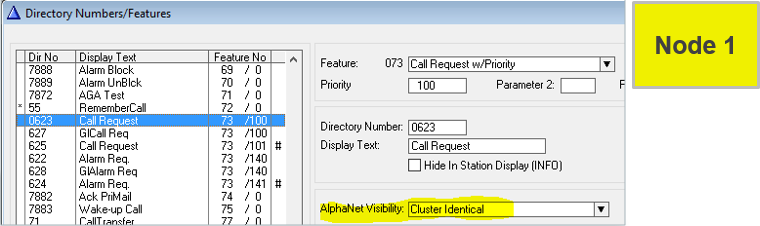
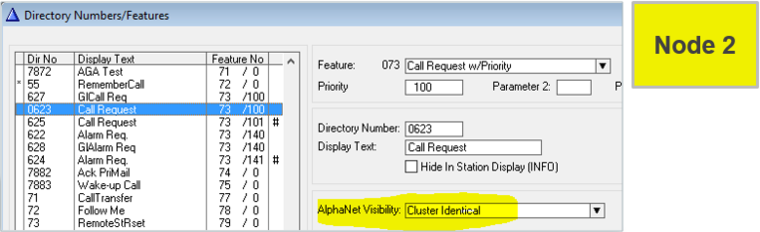
Instead of creating the same local feature in every node, do it once:
- Set Visibility = “Cluster Identical” on a Feature in one node...
...and a copy will automatically be created in all other nodes in the cluster.
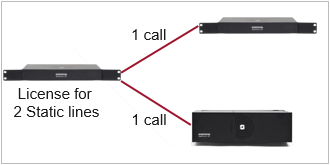
2-line static license - details
An AlphaCom server with a 2-line static license allows maximum two simultaneous AlphaNet calls.
Static Licenses are typically used in:
- Low traffic 2-node system
- AlphaNet with multiple nodes were “end nodes” needs to call central node” only
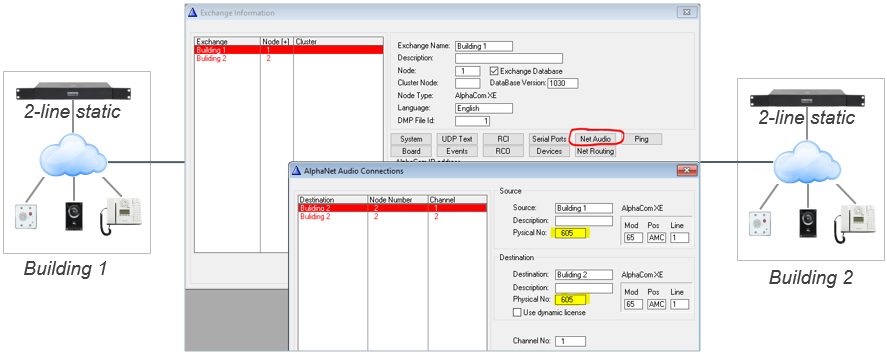
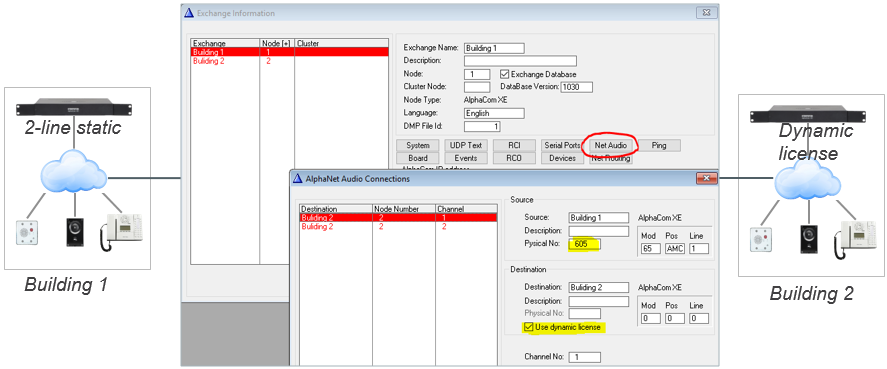
When using AlphaNet Static License, one have to configure fixed Audio Connections between the AlphaCom servers. This is done from AlphaPro, Exchange & System > NetAudio, where you specify that a VoIP channel in the "Source" exchange has a static (fixed) connection to a VoIP channel in the "Destination" exchange.
Each VoIP channel is identified by a virtual physical number:
- VoIP Channel 1 = Physical Number 605
- VoIP Channel 2 = Physical Number 606
- ..
- ..
- VoIP Channel 30 = Physical Number 634
Example - Low traffic 2-node system
Two AlphaCom nodes, both with 2-line Static License
NetAudio configuration:
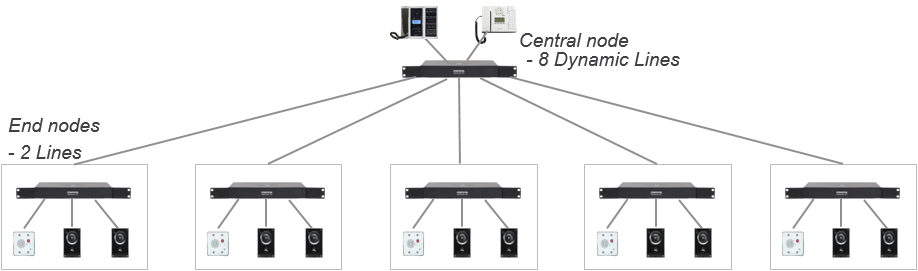
Example - AlphaNet with multiple nodes, “end nodes” needs to call central node” only
NetAudio configuration:
- "NetAudio" must be configured in all "End nodes"
- No configuration of "NetAudio" required in the Central node
License requirements
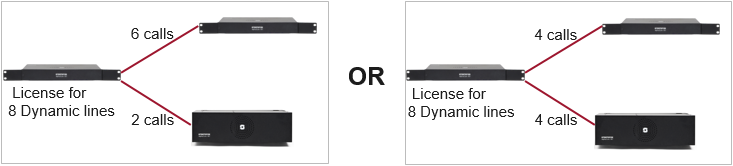
Every node requires an AlphaNet license. The license controls the number of simultaneous calls to and from an AlphaCom. There are two types of AlphaNet license:
- Dynamic license: Pool of VoIP channels - automatically allocated when needed
- Static license: VoIP channels must be fixed towards specific node(s)
See also AlphaNet License
VoIP Bandwidth
AlphaNet provides bandwidth management limiting the VoIP bandwidth to not take more capacity than provisioned.
- Each active call uses approx. 100 kbps
- Maximum bandwidth usage: Number of simultaneous calls x 100 kbps
- Example: System with16 Dynamic Lines
- Max. possible bandwidth usage is 16 x 100 kbps = 1.6 Mbps
Additional information
Priority handling of events and resources
All calls and events that are sent between nodes are marked with priority. This allows the system to act upon the priority, presenting and handling the events and calls in the correct order. If a high priority call is set up when all VoIP channels are occupied, AlphaCom will immediately release the call with the lowest priority allowing the high priority call to proceed.
Alternative routing
Alternative routing of calls allows call completion even when the primary AlphaNet route is down.
Backwards compatibility
AlphaCom provides 100% backwards compatibility between traditional AlphaNet technologies and new VoIP AlphaNet. The backwards compatibility allows mixing of the AlphaCom nodes working over IP with current nodes. This makes the configuration of the system very easy, allowing quick and precise maintenance.
Troubleshooting
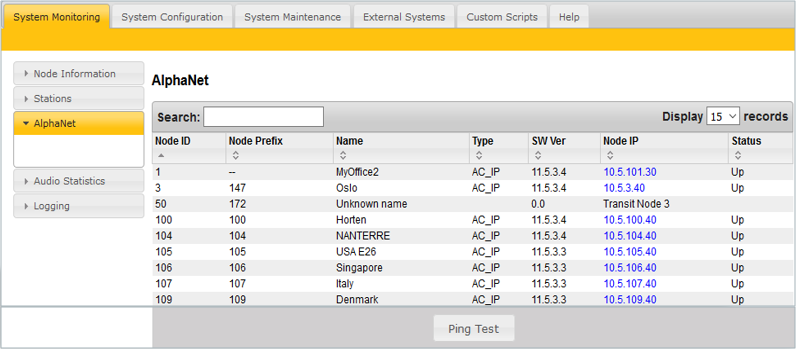
In AlphaWeb, System Monitoring > AlphaNet, some information about the AlphaNet status is listed.
- If the node is listed: Routing information in AlphaPro is correct. If not, check NetRouting in AlphaPro, then do a Send All followed by a reset.
- Press Ping Test to check Status and Ping Time:
- Down, and no answer to Ping: No TCP/IP communication to remote node. Check network, cables, switches etc...
- Down, but Ping time is returned: IP communication is OK, but not AlphaNet. Most likely blocking of TCP port 50000 in internal or external firewall. Check if "AlphaNet" is enabled in Filters.
- Up: AlphaNet communication is OK
Note: The node with the lowest node number is TCP-Client, the highest is TCP-Server.