ICX Web
From Zenitel Wiki
This article describes the web interface of the ICX500 Gateway.
The ICX500 gateway runs an embedded web server. It allows the users to log in using a standard web browser such as Chrome or Firefox to operate and manage the ICX500 system. The web server provides functions for system monitoring, configuration, and software upgrade.
Initial connection
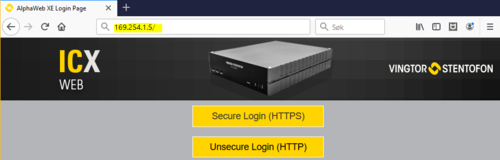
Logging in
Initial connection is done by connecting a laptop to Eth port 0, open a web browser (e.g. Firefox or Chrome), and type in the IP address in the address field of the browser:
- Default IP address 169.254.1.5
- Default Username: admin
- Default Password: alphaadmin
These credentials will give Read/Write privileges, making it possible to do changes in the configuration.
To log in with Read privileges only, the credentials are:
- Default Username: alpha
- Default Password: com
With these credentials one can check status and read information, but not make any changes to the system.
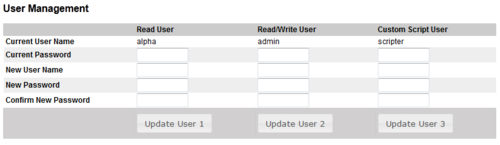
Changing Default User Name and Password
For security reasons it is recommended to change the default user names and passwords.
- Select System Configuration > User Management
- Enter the Current Password for both Read access and Read/Write access (default: com and alphaadmin)
- Enter new User Name and Password
- Re-enter the New Passwords to confirm
- Verify by clicking Update User 1 and Update User 2
- Write down the selected passwords and keep them in a secure place.
Saving and Applying changes
When new configuration parameters are entered, they are saved to the configuration file by clicking Save. To apply the new settings to the running configuration, click Apply.
System Monitoring
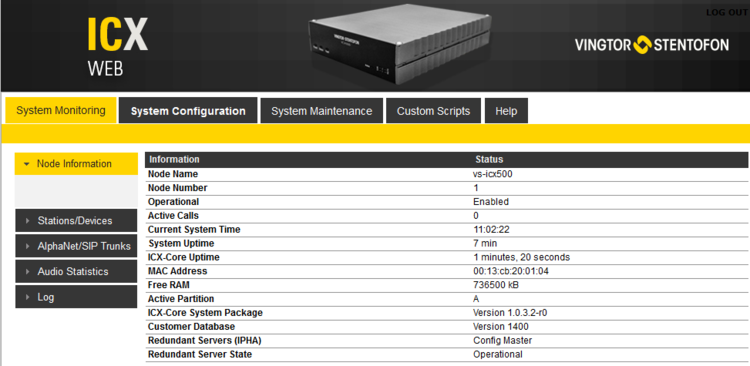
Node Information
Shows general information about the system such as Node Name and Node Number. It also shows state information; different times and memory usage. Information about the Software Configuration, and the Hardware Configuration (the different boards and versions), and also the state of the different processes running in the system.
- Node name: The name of the exchange, as per entered in AlphaPro, Exchange & System > System menu.
- Node number: Default node number is 1. The node number is used for communication between exchanges connected in a network (AlphaNet). The node number can be changed from AlphaPro, Exchange & System > System menu.
- Operational: Enabled: The intercom application (AMCd) is running. Disabled: The intercom application (AMCd) is not running.
- Usage: Shows the number of currently active calls. E.g. Active (2/250) means that there are two active calls in the system. You need to refresh the web page to see current status. If there is a need to restart the system, one can wait until the Usage is Idle (0/250) not to interrupt any ongoing calls.
- Current System Time: Shows the current time in the AlphaCom XE, as presented in display stations.
- System Uptime: The time elapsed since last time the system (Linux) started
- AMC Uptime: The time elapsed since last time the intercom application (AMCd) started
- MAC Address: Shows the MAC address of the AlphaCom XE.
- Total Space (FLASH / DATA FLASH / RAMS): Total memory space.
- FLASH: Memory space for program files, such as Linux and all program modules (AMCd, SIPd, RMd, AlphaWeb etc.)
- DATA FLASH: Memory space for storing of data, such as log files, voice messages and billing data (Not program files)
- RAMFS: RAM File System for storing of temporary data, such as package uploads, web work files, RM- M100- and Billing configuration, various status data.
- Free Space (FLASH / DATA FLASH / RAMS): Available memory space.
- Battery Valid: The state data is stored in RAM memory on the AMC-IP, which is backed up by a battery. Yes means the battery is good, No means the battery must be replaced.
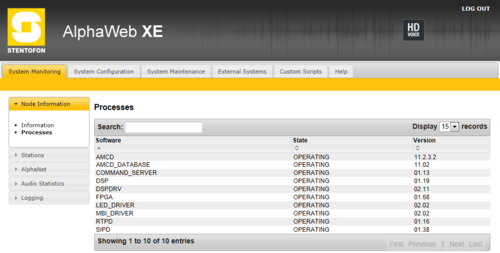
Processes
Shows which software processes are currently running, and the version number of each process.
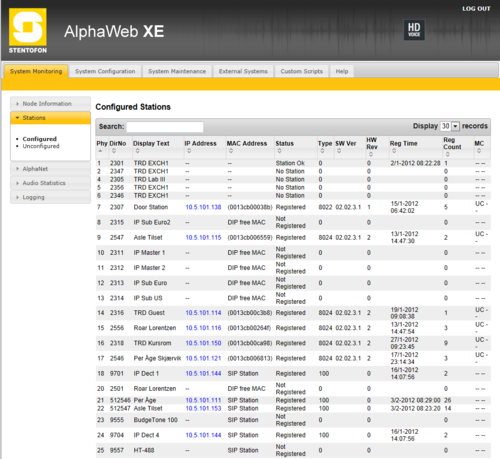
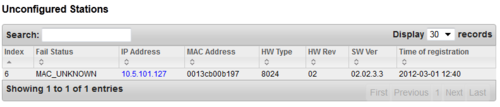
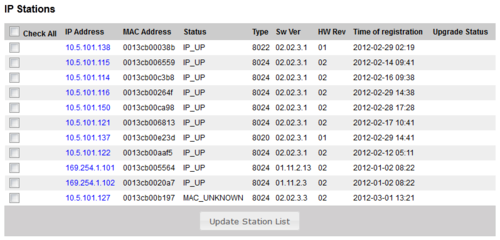
Stations/Devices
The table can be sorted by clicking on the relevant header. In the Search field you can search for any free text, e.g. directory number, display text or IP address.
- Physical Numbers: The physical number is the physical port where an analog station is connected, or a virtual port when using IP station or SIP station.
- Directory Number: The directory number is the number you must dial to reach the station.
- Display Text: The caller ID of the station as programmed in AlphaPro, Users & Stations.
- IP Address: The IP address of the IP Station or SIP Station. Clicking on the IP address will open a new tab in your browser and connect to that IP address.
- MAC Address: This field is relevant for IP stations and SIP stations only.
- (0013cb00c7e9): The MAC address of the IP station. When the MAC address is displayed in brackets with lowercase letters, the station is registered with Directory Number. The MAC address will only show when the station is registered, else it will show DIP free MAC.
- 0013CB00C7E9: The MAC address of the IP station. When the MAC address is displayed without brackets in uppercase letters, the station is configured in AlphaPro to register with its MAC address. The MAC address will show regardless if the station is registered or not.
- DIP free MAC: The IP station is configured in AlphaPro to register with Directory Number, but is not registered.
- SIP Station: The station is configured as a SIP Station in AlphaPro.
- Status
- Station OK: The station is connected and reported OK in the AlphaCom system.
- No Station: An ASLT line card is present, but no station is found.
- Station Failure: The station has been registered to the Alphacom, but connection is now lost.
- Not Registered: The IP station or SIP station is configured in the system, but has not been able to register to the AlphaCom.
- Registered: The IP station or SIP station has successfully registered to the AlphaCom.
- No License: The registration was rejected due to missing licenses.
- Type: Shows what type of equipment which is connected/registered.
- Analog stations is shown as 0
- IP Stations - Shows which type of IP station
- 8020 - Dual Display Stations
- 8022 - Sub Stations
- 8023 - Flush Master Stations
- 8024 - Desk Master Stations
- 8026 - IP ARIO
- 8300 - Turbine station
- 100 - SIP Phone/Station
- SW Ver: Software Version. Shows the IP station software version. Applicable to IP stations only.
- HW Rev: Hardware Revision. Shows the IP station hardware version. Applicable to IP stations only.
- Reg Time: Registration Time. Shows the last time the station registered to the AlphaCom.
- Reg Count: Registration Counter. Shows the number of times a station has registered to the Alphacom since last reset.
- MC: MultiCast. Status information about Group Audio configuration (Groupcall, Audio Program, Simplex Conference) and status of the IP station.
- UC: Unicast
- M0 or M1: Direct multicast on ethernet ports 0 or 1
- R0 to R4: Relayed multicast to Group 0 to 4
- See Multicast in AlphaCom for more details.
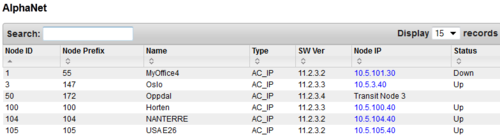
AlphaNet
This tab gives an overview over the AlphaNet. The list is ascending according to the Node number. The list will show:
- The Node Number
- The Node Name
- The Node Type
- 2 = AlphaCom E
- 3 = SIP node
- Software Version (AMC sowftare version on the nodes AMC-IP card).
- The Node IP Address
- Status (Shows the communication state to the other Nodes in the AlphaNet.
Audio Statistics
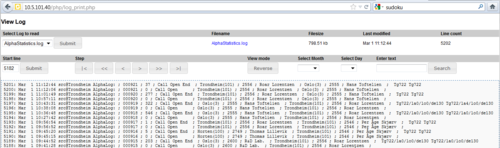
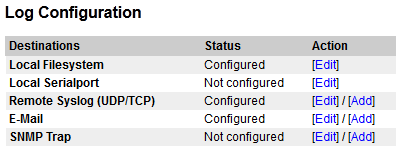
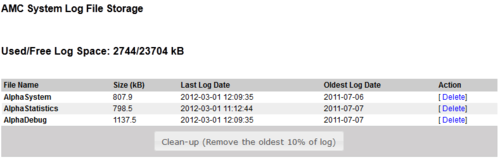
Logging
Logging can be setup to:
- Serial ports
- Local file on AMC-IP
- Syslog
- SNMP trap (MIB II)
- Or to all above simultaneously
Three different log types are available:
- -Low level DP messages (like in TST error buffer)
-Messages from amcd, rtpd, amc_initd, amc_netconfig, kern, daemons
- -RCI activations, error reports, log port, AlphaPro IP login
-Amcd user, log and events
- -All converstations (start - end)
No log-streams are default. It must be configured in System configuration/Logging. Deletion is also done here.
”Pri Level” is only available for the technical log (info = all).
Syslog is a standard for sending log-information over Ethernet.
On-board logs are viewed in System Monitoring/logging.
System Configuration
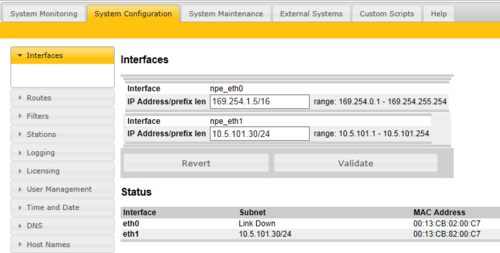
Interfaces
There are two Ethernet interfaces on the AlphaCom, Eth0 and Eth1.
As from software version 11.3.3.2, the IP address is set by using CIDR notation. It appends a slash character ("/") to the address and a decimal number specifying the number of bits (out of the total 32 bits of an IP address) that the network prefix consists of.
After the IP address is entered in CIDR notation, press Validate, and then Save & Apply.
Examples of CIDR notation and equivalent dot-decimal notation:
- 169.254.1.5/16 is equivalent to IP address 169.254.1.5 and net mask 255.255.0.0.
- 10.5.101.30/24 is equivalent to IP address 10.5.101.30 and net mask 255.255.255.0.
- 192.168.1.40/26 is equivalent to IP address 192.168.1.40 and net mask 255.255.255.192.
See here for more examples.
In software versions prior to 11.3.3.2, the IP Address was defined by using dot-decimal notation for both the address and the net mask. Remember to press Apply after Save.
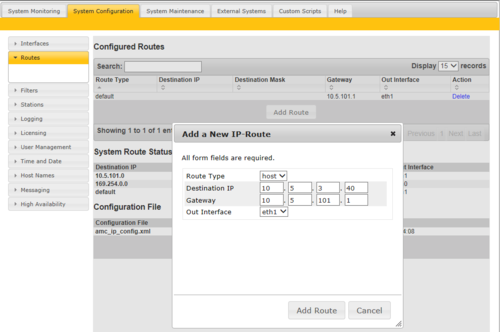
Routes
The IP Routing table of the AlphaCom must be configured if there is a need to communicate with devices outside its own subnet. A “device” could be another AlphaCom, a PC (AlphaPro, AlphaWeb, SysLog), SIP equipment, Ethernet to Serial device etc. If there is no need for communication outside own subnet, there is no need to define any routing.
Three different route types can be defined:
- Default route (= Default gateway)
- Net route - A route to one particular IP network
- Host route - A route to one particular host
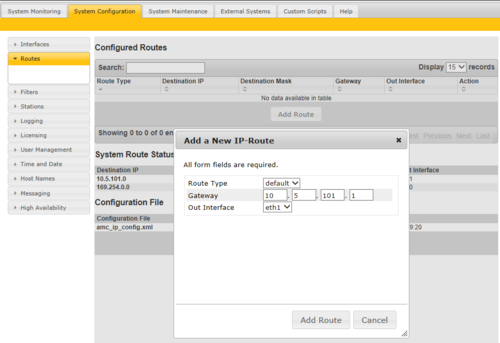
Defining a Default Gateway
Only one Default Gateway can be defined.
To define a Default Gateway (Software version 11.3.3.2 and later), select Add New, and enter:
- Destination net = 0.0.0.0/0
- Gateway on local subnet = IP Address of the default gateway
- Interface = On which Ethernet interface the default gateway is located
- Press Validiate
- Press Save & Apply
To define a Default Gateway on software version prior to 11.3.3.2, select Add Route, and enter:
- Route type = Default
- Gateway = IP Address of the default gateway
- Out interface = On which Ethernet interface the default gateway is located
- Press Add Route
- Press Apply
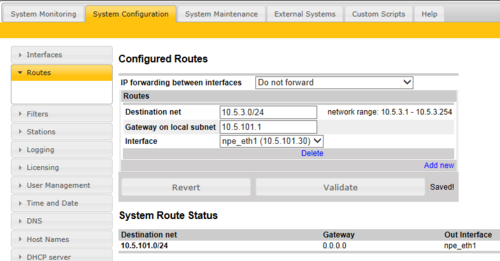
Defining a Net Route
To define a route to one particular network (Software version 11.3.3.2 and later), select Add New, and enter:
- Destination net = IP address of the remote IP network in CIDR notation
- Gateway on local subnet = IP Address of the gateway
- Interface = On which Ethernet interface the gateway is located
- Press Validiate
- Press Save & Apply
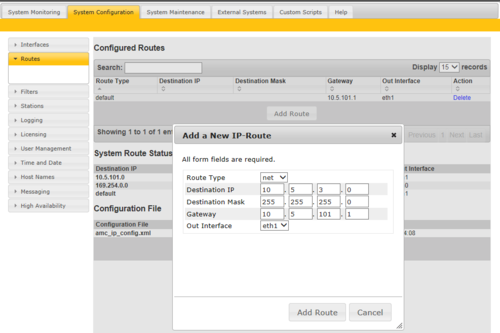
To define a net route on software version prior to 11.3.3.2, select Add Route, and enter:
- Route Type = Net
- Destination IP = IP Address of the network
- Destination Mask = The net mask of the destination network
- Gateway = IP Address of the gateway
- Out Interface = On which Ethernet interface the gateway is located
- Press Add Route
- Press Apply
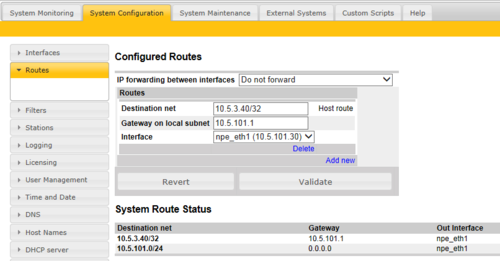
Defining a Host Route
To define a Host route (Software version 11.3.3.2 and later), select Add New, and enter:
- Destination net = <IP address of the host>/32
- Gateway on local subnet = IP Address of the gateway
- Interface = On which Ethernet interface the gateway is located
- Press Validiate
- Press Save & Apply
To define a route to a host on software version prior to 11.3.3.2, select Add Route, and enter:
- Route type = Host
- Destination IP = The IP address of the host
- Gateway = IP Address of the gateway
- Out interface = On which Ethernet interface the gateway is located
- Press Add Route
- Press Apply
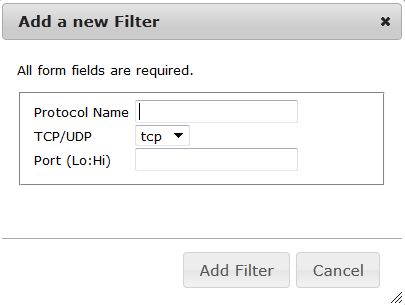
Filters
The Filter is the AlphaCom's own firewall and must be configured when adding equioment that is supposed to communicate with the AlphaCom. Applications port number can be enabled on both ethernet ports. All ports except port 80 and 443 (AlphaWeb) can be deleted
And new application port numbers can be added. Remember to enable it after adding!
Stations
Logging
There are three different log types:
- System Log
- RCI activations, error reports, log port, AlphaPro IP login
- Amcd user, log and events
- Call Statistics Log
- All logins and authentications of users, stations, administrators...
- All conversations (start - end)
- Debug Log
- Low level messages (like in TST error buffer)
- Messages from amcd, rtpd, amc_initd, amc_netconfig, kern, daemons. For debugging purposes for software engineers.
The log information can be sent to:
- Serial ports
- Local file on AMC-IP
- SysLog
- SNMP trap (MIB II)
- Or to all above simultaneously
Log rotation:
The log system is creating a new file every day for each of the log types (Debug, System and Statistics).
Every 10 minutes there is a check if the log files are consuming more than 3MB of memory space. If more than 3MB, the oldest log file will be deleted, until the remaining space is below 3MB. I.e. you will loose one day of logging each time a log file is deleted.
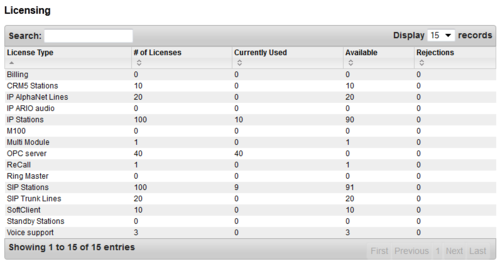
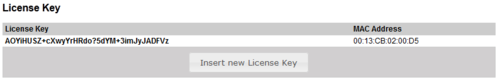
Licensing
Licences for IP AlphaNet, IP stations and SIP audio links are added in System configuration/License Key. License Key is linked to the unique MAC address of the AMC
From AMC10.0.5 it is not necessary to configure audio routing because dynamic is default.
- The exception is 2 line static license
AlphaNet, Multi-module and SIP licenses are in a pool.
- All links without Net-Audio and Net-Routing are assumed to be Multi-module
- If a static audio route is configured, it is taken out of the pool
”Currently used” shows links in use at the moment. ”Rejections” count up how many operations that are rejected due to no more available licenses.
User Management
It is highly recommended to change username and password. This is done in System configuration/User management
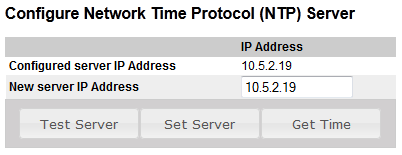
Time and Date
The real-time clock in AlphaCom can be synchronised to a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server. This is set up in System configuration -> Time manager.
The button "Get Time" will read the NTP time and set the AMC realtime clock.
The clock is automatically syncronized once an hour (20 minutes past the hour).
DNS
Hostnames
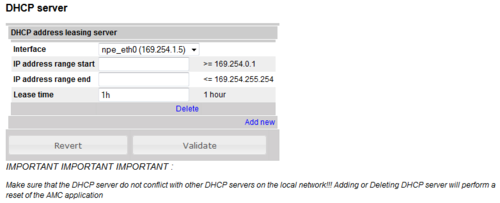
DHCP server
Messaging
Only for black (AMC11) AMC-IP boards.
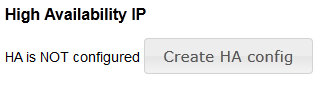
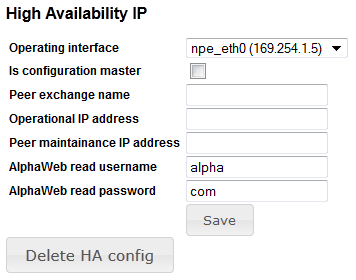
High Availability
Only for black (AMC11) AMC-IP boards.
System Maintenance
System Upgrade
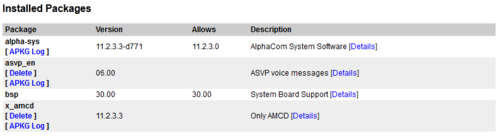
AMC software is upgraded in System upgrade.
Browse for the new software and do an upload to AMC-IP.
Then do a ”Select” and ”Install Selected”
For details se AMC-IP software upgrade
See also AlphaCom E Software packages
IP Station Upgrade
IP Station Discovery:
To search for IP Stations in the range 10.5.101.100 to 10.5.101.200, enter:
- Class C Network: 10.5.101
- Subnet Start: 100
- Subnet End: 200
A list of stations will appear when the search is finnished. By clicking on the IP address in the list you will be connected to the web server of that station.
Config Backup
This is performed in System Maintenance/Backup
The "Create Backup" button will update the backup.bin in AMC.
You will simultaneously be asked if you want to store the file to your PC/server. This will be an .apkg file containing both IP setteings and the Database.
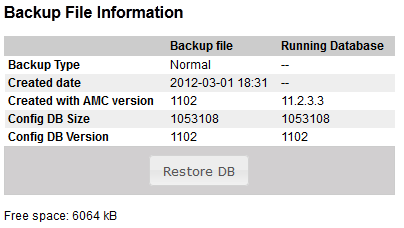
The "Restore DB" button is used to restore the Database from the onboard memory.
See also: Backup
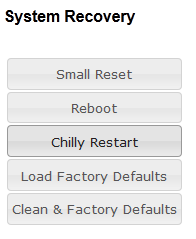
System Recovery
- Small Reset: Reset main applications
- Reboot: Reboots the system
- Chilly Restart: Reset main applications and clear state data like mails, transfers, absense, %udd and program selection. Configuration data are kept.
- Load Factory Default: Reset intercom configuration data. IP settings are kept.
- Clean & Factory Defaults: Reset intercom configuration data. Remove License, SysLog and Backup files. IP settings are kept.
Station Discovery (Beta)
See article IP station Discovery and Initial Configuration from AlphaWeb.
Help
Backup and Restore
Create Backup
Navigate to System Maintenance -> Backup and click Create Backup.
An AlphaPro backup file will be stored in the on-board flash memory (same as dialling 7820). You will be prompted to store a full backupfile (AlphaPro and AlphaWeb settings) on your computer.
Store configuration to AMC Flash Memory from station: 7820 + M Restore configuration from AMC Flash Memory from station: 7819 + M
Restore Backup from AMC
The AlphaPro configuration can be restored from the AMC-IP onboard memory by dialling 7819 + M on a superuser station. It can also be restored in AlphaWeb:
Navigate to System Maintenance -> Backup and click Restore DB.
Restore full Backup from PC
The full backup containing both AlphaPro and AlphaWeb settings must be uploaded, installed and activated in AlphaWeb.
Navigate to System Maintenance -> System Upgrade and click Browse. Browse your computer for the correct backup file and select Upload.
Two files will now appear:
- Select the first file. Click the Install button that becomes available.
- After the installation is done, repeat for the second file.
- Navigate to System Mainteneance -> Backup and click Restore DB. This will restore the AlphaPro database.
- Navigate to System Configuration -> Interfaces and press Save followed by Apply and confirm with Yes. This will activate all the AlphaWeb settings.
- Navigate to System Maintenance -> System Recovery and click Reboot. Reboots the system to make all changes take full effect.