RCO - Remote Control Output
From Zenitel Wiki
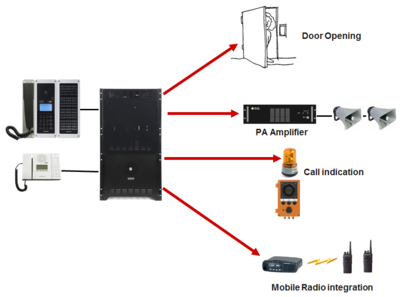
The Remote Control Output RCO’s are used to operate relays for control of external equipment.
Relay outputs are typically used for:
- Door opening
- PA control
- Call indication
- Queue indication
- Keying of mobile radio transmitter
- CCTV interface
Contents
Devices supporting RCO’s
- RCO outputs are available on a number of devices:
| Device | # of RCO's | Comment | Hardware required |
|---|---|---|---|
| AlphaCom XE26 | 138 | 6 RCOs per ASLT card or ATLB-12 card | MRBD relay board + PDB Power Distribution Board |
| AlphaCom XE20 | 102 | 6 RCOs per ASLT card or ATLB-12 card | MRBD relay board |
| AlphaCom XE7 | 12 | Need ASLT in position 1 and/or 2 | MRBD relay board |
| AlphaCom XE1 | 0 | RCOs not available. Use IPARIO unit | IPARIO unit |
| IPARIO unit (IP) | 8 | Remote outputs over IP network | IPARIO unit |
| RIO unit (analog) | 18 | Remote outputs over RS232/485 | MRBD relay board |
| IP Substation board (PCB 8022) | 2 | One relay on connector P3, pin 3/4 | The second output is a logical signal. Transistor + relay required |
| IP Flush Master/IP OR station (PCB 8024) | 2 | One relay on connector P3, pin 3/4 | The second output is a logical signal. Transistor + relay required |
| Turbine Compact/TKIS-2 kit | 7 | One relay included | Use MRBD relay board if more than 1 relay is needed |
Configuration
There are several ways to control RCOs, the most commonly used one is to use Logical RCOs controlled by the RCO command
Logical RCOs
- The RCO command operates a Logical RCO
- Each logical RCO must be mapped to a Device or Station, and to a Pin Number
- The AlphaCom XE software supports up to 500 logical RCOs.
- The operation of the logical RCOs is configured from AlphaPro, in the Event Handler window.
Mapping of RCOs
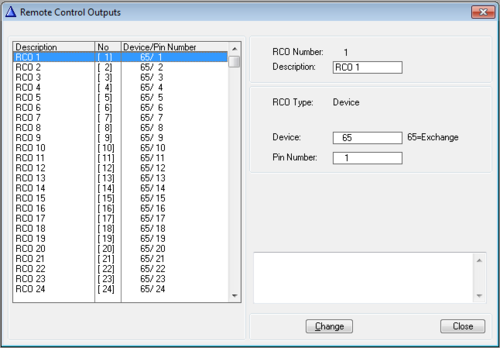
The mapping of RCOs are done from AlphaPro, Exchange & System -> RCO window where the logical RCO is assigned to a physical address. The physical address is given as Device + Pin Number or by Station + Pin Number.
| RCO number: | The "logical" number of the RCO. Use this number in the RCO command. |
| Description: | Any text. This information is stored in the AlphaPro database only, and is not sent to the exchange. |
| RCO Type: | Device: The AlphaCom (i.e. ASLT or ATLB-12 board) or RIO unit Station: IP Station or IPARIO |
| Device: |
|
| Pin number: |
|
The outputs can be used freely within the whole exchange, regardless of physical connections of the stations.
The exchange always keeps track of the state of an output in case the device becomes faulty. When a faulty device becomes OK again, the exchange will restore the RCOs.
Configuration examples
The Event Handler is used to configure the behavior of the RCOs. Here are some examples:
- Door opening and Code lock
- Call indication
- CCTV integration using relays
- CCTV control by relays (RCO) when using Call Request
Additional Information
- For internal RCOs (ASLT/ATLB), the device address is 65, and the pin number is the same as the Physical number of stations, 1 - 552.
- When the ATLB board is used in AlphaCom E7 only four RCO's are available
- Mappings for the internal RCOs in the master are autoloaded. Mappings for RCOs in slave modules, RIO units and IP stations must be manually programmed.
- In an AlphaNet installation you can control RCOs in a remote exchange.
Software
- AMC 10.50 or later to control RCOs in slave modules. Earlier AMC versions support RCOs in master module only (pin 1 - 138).
- AMC 10.04: Additional parameter to pulse the RCO ('RCO 12 ON 20' to generate a 2.0 sec pulse on RCO 12)
- AMC 07.40 or later to control RCOs in an AlphaNet installation.