Difference between revisions of "SIP Intercom - Web Interface"
From Zenitel Wiki
(Created page with "{{S}} thumb|400px|SIP based System Turbine and INCA stations can be...") |
ZenitelAus (talk | contribs) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
The stations are easy to install and configure. They can be configured using a standard web browser (like Firefox or Chrome), or one can use the dedicated [[IMT|Intercom Management Tool IMT]]. This article describes configuration using the Web interface. | The stations are easy to install and configure. They can be configured using a standard web browser (like Firefox or Chrome), or one can use the dedicated [[IMT|Intercom Management Tool IMT]]. This article describes configuration using the Web interface. | ||
| − | = Getting Started = | + | =Getting Started= |
Main steps to get the station registered to a SIP server: | Main steps to get the station registered to a SIP server: | ||
| − | # [[Logging into an IP Station|Log on to the station]] | + | |
| − | # [[Main Settings (IP Stations)|Main Settings]]: Go to '''Station Main''' > '''Main Settings''' and set "Station Mode" = '''Use SIP''', and enter the IP Settings. | + | #[[Logging into an IP Station|Log on to the station]] |
| − | # [[Account Settings (SIP)|Account Settings]]: Select '''SIP Configuration''' > '''SIP Settings''' and enter as a minimum '''Display Name''', '''Directory Number''', '''Server Domain''' and '''Authentication User Name'''. | + | #[[Main Settings (IP Stations)|Main Settings]]: Go to '''Station Main''' > '''Main Settings''' and set "Station Mode" = '''Use SIP''', and enter the IP Settings. |
| − | # [[Direct Access Key & Ringlist Settings (SIP)|Call Buttons (DAK keys)]]: Select '''SIP Configuration''' > '''Direct Access Key Settings'''. | + | #[[Account Settings (SIP)|Account Settings]]: Select '''SIP Configuration''' > '''SIP Settings''' and enter as a minimum '''Display Name''', '''Directory Number''', '''Server Domain''' and '''Authentication User Name'''. |
| − | ## [[OLED Labels]]: How to configure the OLED display used for labeling the call buttons in the station models [[TCIV-5+]], [[TCIS-4]] and [[TCIS-5]] | + | #[[Direct Access Key & Ringlist Settings (SIP)|Call Buttons (DAK keys)]]: Select '''SIP Configuration''' > '''Direct Access Key Settings'''. |
| − | ## [[Address Book]]: How to configure and maintain the Address Book used in the station models [[TCIV-6+]], [[TCIS-6]] and [[TCIV-6]] | + | ##[[OLED Labels]]: How to configure the OLED display used for labeling the call buttons in the station models [[TCIV-5+]], [[TCIS-4]] and [[TCIS-5]] |
| + | ##[[Address Book]]: How to configure and maintain the Address Book used in the station models [[TCIV-6+]], [[TCIS-6]] and [[TCIV-6]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | = The station web interface = | + | =The station web interface= |
| − | == Station Main == | + | ==Station Main== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *'''Station Information''' page shows current status and information about the station, suuch as firmware version and IP Address | ||
| + | *[[Main Settings (IP Stations)|Main Settings]]: Here the mode of operation is set, the network settings, and the model type. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === Audio Settings === | + | ==SIP Configuration== |
| + | ===SIP Settings=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Account Settings (SIP)|Account Settings]]: Configure relevnt parameters for the SIP account | ||
| + | *[[Call Settings (SIP)|Call Settings]]: A number of Call related parameters are available | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Audio Settings=== | ||
[[Audio Settings (SIP)|Audio Settings]]: A number of Audio related parameters are available | [[Audio Settings (SIP)|Audio Settings]]: A number of Audio related parameters are available | ||
| − | ===Direct Access Key & Ringlist Settings === | + | ===Direct Access Key & Ringlist Settings=== |
| − | * '''Direct Access Keys (DAK)''' are the Call Buttons or speed-dial buttons you find on most intercom stations. | + | |
| − | * '''Ring List''' is used to configure Call Escalation (i.e. forwarding of unattended calls), and for Parallel Ringing. | + | *'''Direct Access Keys (DAK)''' are the Call Buttons or speed-dial buttons you find on most intercom stations. |
| + | *'''Ring List''' is used to configure Call Escalation (i.e. forwarding of unattended calls), and for Parallel Ringing. | ||
To configure Call Buttons and Ring List, see [[Direct Access Key & Ringlist Settings (SIP)]] | To configure Call Buttons and Ring List, see [[Direct Access Key & Ringlist Settings (SIP)]] | ||
| − | === Relay/Output Settings === | + | ===Relay/Output Settings=== |
All IP Intercom stations (execpt the desktop models) have a built-in relay which can be used for door opening, call indication lamp etc. The relay can be controlled by a DTMF digit, or by a number of different call events and station statuses. | All IP Intercom stations (execpt the desktop models) have a built-in relay which can be used for door opening, call indication lamp etc. The relay can be controlled by a DTMF digit, or by a number of different call events and station statuses. | ||
For details about relay configuration, see [[Relay Settings (SIP)|Relay Settings]] | For details about relay configuration, see [[Relay Settings (SIP)|Relay Settings]] | ||
| − | === Time Settings=== | + | ===Time Settings=== |
The user is able to configure time by either enabling NTP and specifying NTP server, or setting up time manually. On Master stations with display the configured time is shown on display. | The user is able to configure time by either enabling NTP and specifying NTP server, or setting up time manually. On Master stations with display the configured time is shown on display. | ||
See [[Time Settings (SIP)|Time Settings]] for details. | See [[Time Settings (SIP)|Time Settings]] for details. | ||
| − | === I/O Settings === | + | ===I/O Settings=== |
The [[:Category:Stations#Turbine_stations|Turbine stations]] have 6 I/O's which can be used as Inputs or Outputs. By default all I/O's are set as Inputs. | The [[:Category:Stations#Turbine_stations|Turbine stations]] have 6 I/O's which can be used as Inputs or Outputs. By default all I/O's are set as Inputs. | ||
For details about configuration of inputs and outputs, see [[I/O Settings (SIP)|I/O Settings]]. | For details about configuration of inputs and outputs, see [[I/O Settings (SIP)|I/O Settings]]. | ||
| − | === Frontboard Mapping [Turbine only]=== | + | ===Frontboard Mapping [Turbine only]=== |
When making customized stations based on the Turbine Frontboard, it is possible from the station web interface to define DAK actions and LED behavior. | When making customized stations based on the Turbine Frontboard, it is possible from the station web interface to define DAK actions and LED behavior. | ||
This is supported when front board type is set to TCIS 1/2/3 and TCIV 1/2/3, and the station operates in Pulse or SIP mode. | This is supported when front board type is set to TCIS 1/2/3 and TCIV 1/2/3, and the station operates in Pulse or SIP mode. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 61: | ||
For more details, see [[Button and LED configuration for customized stations (SIP)]] | For more details, see [[Button and LED configuration for customized stations (SIP)]] | ||
| − | === RTSP and ONVIF (Non video intercoms) === | + | ===RTSP and ONVIF (Non video intercoms)=== |
'''RTSP Settings''': see [[RTSP_Settings#Non-Video_Intercoms|RTSP Settings for Non-Video Intercoms]] | '''RTSP Settings''': see [[RTSP_Settings#Non-Video_Intercoms|RTSP Settings for Non-Video Intercoms]] | ||
'''ONVIF Settings''': see [[ONVIF_Settings#Non_Video_Intercoms|ONVIF Settings for Non-Video Intercoms]] | '''ONVIF Settings''': see [[ONVIF_Settings#Non_Video_Intercoms|ONVIF Settings for Non-Video Intercoms]] | ||
| − | === Video Settings === | + | ===Video Settings=== |
See article [[Video Settings]] on how to set parameters for the camera and stream options. | See article [[Video Settings]] on how to set parameters for the camera and stream options. | ||
| − | === Advanced Video Settings === | + | ===Advanced Video Settings=== |
'''RTSP Settings''': see [[RTSP_Settings#Video_Intercoms|RTSP Settings for Video Intercoms]] | '''RTSP Settings''': see [[RTSP_Settings#Video_Intercoms|RTSP Settings for Video Intercoms]] | ||
'''ONVIF Settings''': see [[ONVIF_Settings#Video_Intercoms|ONVIF Settings for Video Intercoms]] | '''ONVIF Settings''': see [[ONVIF_Settings#Video_Intercoms|ONVIF Settings for Video Intercoms]] | ||
| − | === Scripts [Turbine only]=== | + | ===Scripts [Turbine only]=== |
'''Scripts''' (Virtual I/O) is a feature for activating scripts on station events. The supported script languages are Lua and other shell scripting languages. This can be used for example to execute scripts towards other systems, e.g. access control systems, triggered by a DTMF digit. These scripts can be uploaded and configured via the menu options: | '''Scripts''' (Virtual I/O) is a feature for activating scripts on station events. The supported script languages are Lua and other shell scripting languages. This can be used for example to execute scripts towards other systems, e.g. access control systems, triggered by a DTMF digit. These scripts can be uploaded and configured via the menu options: | ||
| − | * Script Upload | + | |
| − | * Script Configuration | + | *Script Upload |
| − | * Script Events | + | *Script Configuration |
| + | *Script Events | ||
The Scripting feature is supported on [[:Category:Stations#Turbine_stations|Turbine stations]] only. | The Scripting feature is supported on [[:Category:Stations#Turbine_stations|Turbine stations]] only. | ||
| Line 80: | Line 85: | ||
For more details, see [[Virtual I/O (SIP)|Virtual I/O]] | For more details, see [[Virtual I/O (SIP)|Virtual I/O]] | ||
| − | === Audio Messages [Turbine only]=== | + | ===Audio Messages [Turbine only]=== |
Prerecorded audio files can be uploaded to a [[:Category:Stations#Turbine_stations|Turbine IP Station]], and the audio messages can be triggered by various events occuring on the station. The audio message files are uploaded from the station webinterface or from the [[IMT|VS-IMT tool]]. | Prerecorded audio files can be uploaded to a [[:Category:Stations#Turbine_stations|Turbine IP Station]], and the audio messages can be triggered by various events occuring on the station. The audio message files are uploaded from the station webinterface or from the [[IMT|VS-IMT tool]]. | ||
See [[Audio Messaging (SIP)|Audio Messaging]] for more details. | See [[Audio Messaging (SIP)|Audio Messaging]] for more details. | ||
| − | === Multicast Paging === | + | ===Multicast Paging=== |
'''Multicast Paging''' enables IP intercom stations in SIP mode to receive VoIP audio as multicast paging from 3rd party iPBX (e.g. Asterisk). The feature is supported by both [[:Category:Stations#INCA_stations|INCA stations]] and [[:Category:Stations#Turbine_stations|Turbine stations]]. Up to 10 different Multicast paging groups can be defined. | '''Multicast Paging''' enables IP intercom stations in SIP mode to receive VoIP audio as multicast paging from 3rd party iPBX (e.g. Asterisk). The feature is supported by both [[:Category:Stations#INCA_stations|INCA stations]] and [[:Category:Stations#Turbine_stations|Turbine stations]]. Up to 10 different Multicast paging groups can be defined. | ||
| Line 92: | Line 97: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | == Station Administration == | + | ==Station Administration== |
| − | === Logging === | + | ===Logging=== |
Logs can be useful for debugging and troubleshooting purposes. See [[Logging - IP Stations]] on how to enable and collect logs. | Logs can be useful for debugging and troubleshooting purposes. See [[Logging - IP Stations]] on how to enable and collect logs. | ||
| − | === Change Password=== | + | ===Change Password=== |
The password for web access and for accessing the display setup menus can be changed, see [[Password (IP Stations)]]. | The password for web access and for accessing the display setup menus can be changed, see [[Password (IP Stations)]]. | ||
| − | === Backup and Restore === | + | ===Backup and Restore=== |
From the web interface of the station it is possible to backup and restore the configuration data. See [[Backup and Restore (IP Stations)|Backup and Restore]] for more information. | From the web interface of the station it is possible to backup and restore the configuration data. See [[Backup and Restore (IP Stations)|Backup and Restore]] for more information. | ||
| − | === Manual Upgrade === | + | ===Manual Upgrade=== |
The software in the stations can be upgraded via the web interface of the station. The procedure is slighty different depending on the type of station: | The software in the stations can be upgraded via the web interface of the station. The procedure is slighty different depending on the type of station: | ||
| − | * [[:Category:Stations#Turbine_stations|Turbine devices]]: [[Turbine Software Upgrade|Upgrade procedure]] | + | |
| − | * [[:Category:Stations#INCA_stations|INCA devices]]: [[INCA Station Software upgrade|Upgrade procedure]] | + | *[[:Category:Stations#Turbine_stations|Turbine devices]]: [[Turbine Software Upgrade|Upgrade procedure]] |
| + | *[[:Category:Stations#INCA_stations|INCA devices]]: [[INCA Station Software upgrade|Upgrade procedure]] | ||
===Language Settings [INCA only]=== | ===Language Settings [INCA only]=== | ||
In the [[:Category:Stations#INCA_stations|INCA type stations]] it is possible to change the language of the display texts. This does not affect the texts in the web server interface. See [[Language Settings (SIP)|Language Settings]] for details. | In the [[:Category:Stations#INCA_stations|INCA type stations]] it is possible to change the language of the display texts. This does not affect the texts in the web server interface. See [[Language Settings (SIP)|Language Settings]] for details. | ||
| − | === Keyboard [INCA only]=== | + | ===Keyboard [INCA only]=== |
On the [[:Category:Stations#INCA_stations|INCA Stations]] there is an option to set Keyboard Type. This is typically used for the [[IP Substation Kit - 1008090200|IP Substation kit]] or the [[IP Master Station Kit - 1008093000|IP Master kit]] when building customized stations. See [[Keyboard Settings]] for further details. | On the [[:Category:Stations#INCA_stations|INCA Stations]] there is an option to set Keyboard Type. This is typically used for the [[IP Substation Kit - 1008090200|IP Substation kit]] or the [[IP Master Station Kit - 1008093000|IP Master kit]] when building customized stations. See [[Keyboard Settings]] for further details. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | == Advanced SIP == | + | ==Advanced SIP== |
| − | === Updates (TFTP Provisioning) === | + | ===Updates (TFTP Provisioning)=== |
IP stations may be set up to automatically poll configuration from a TFTP server. The IP address of this TFTP server can be obtained using DHCP procedures or be manually configured. See [[TFTP Provisioning (SIP)|TFTP Provisioning]] for more information. | IP stations may be set up to automatically poll configuration from a TFTP server. The IP address of this TFTP server can be obtained using DHCP procedures or be manually configured. See [[TFTP Provisioning (SIP)|TFTP Provisioning]] for more information. | ||
| − | === Tone test === | + | ===Tone test=== |
The '''tone test''' is designed to check whether the microphone and loudspeaker is working by playing a tone and detecting the sound pressure level. If the sound pressure level is below a chosen threshold the test fails. The result of the tone test is reported using SNMP traps, which must be turned on in the [[SNMP in IP Stations|SNMP configuration]]. | The '''tone test''' is designed to check whether the microphone and loudspeaker is working by playing a tone and detecting the sound pressure level. If the sound pressure level is below a chosen threshold the test fails. The result of the tone test is reported using SNMP traps, which must be turned on in the [[SNMP in IP Stations|SNMP configuration]]. | ||
For configuration of the Tone test, see [[Tone Test (IP Stations)]] | For configuration of the Tone test, see [[Tone Test (IP Stations)]] | ||
| − | === Web Call === | + | ===Web Call=== |
Webcall makes it possible to establish a call directly from the station web. See [[Web Call and HTTP commands (SIP)|Web Call]] for more information. | Webcall makes it possible to establish a call directly from the station web. See [[Web Call and HTTP commands (SIP)|Web Call]] for more information. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | == Advanced Network Settings == | + | ==Advanced Network Settings== |
| − | === SNMP === | + | ===SNMP=== |
A set of SNMP functions are available in the IP station. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol for centralizing the management of devices in IP networks. | A set of SNMP functions are available in the IP station. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol for centralizing the management of devices in IP networks. | ||
See [[SNMP in IP Stations]] for futher information. | See [[SNMP in IP Stations]] for futher information. | ||
| − | === 802.1X === | + | ===802.1X=== |
IEEE 802.1X is an IEEE Standard for port-based Network Access Control (PNAC). It provides an authentication mechanism to devices wishing to attach to a LAN, either establishing a point-to-point connection or preventing it if authentication fails. For details on configuration, see [[IEEE 802.1X]]. | IEEE 802.1X is an IEEE Standard for port-based Network Access Control (PNAC). It provides an authentication mechanism to devices wishing to attach to a LAN, either establishing a point-to-point connection or preventing it if authentication fails. For details on configuration, see [[IEEE 802.1X]]. | ||
| − | ===Firewall === | + | ===Firewall=== |
All IP Stations have an embedded firewall. See [[Firewall (IP Stations)|Firewall]] for details. | All IP Stations have an embedded firewall. See [[Firewall (IP Stations)|Firewall]] for details. | ||
| − | === VLAN Tagging [INCA only] === | + | ===VLAN Tagging [INCA, IPDM and IPDMH only]=== |
'''VLAN Tagging''' is the practice of inserting a '''VLAN ID''' into a packet header in order to identify which '''VLAN''' (Virtual Local Area Network) the packet belongs to. More specifically, switches use the '''VLAN ID''' to determine which port(s), or interface(s), to send a broadcast packet to. | '''VLAN Tagging''' is the practice of inserting a '''VLAN ID''' into a packet header in order to identify which '''VLAN''' (Virtual Local Area Network) the packet belongs to. More specifically, switches use the '''VLAN ID''' to determine which port(s), or interface(s), to send a broadcast packet to. | ||
For details on configuration, see [[VLAN Tagging (IEEE 802.1Q)]]. | For details on configuration, see [[VLAN Tagging (IEEE 802.1Q)]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category: INCA Station Configuration Guide]] | [[Category: INCA Station Configuration Guide]] | ||
[[Category: SIP intercom - Configuration]] | [[Category: SIP intercom - Configuration]] | ||
[[Category: Turbine Configuration]] | [[Category: Turbine Configuration]] | ||
Revision as of 07:12, 15 July 2022
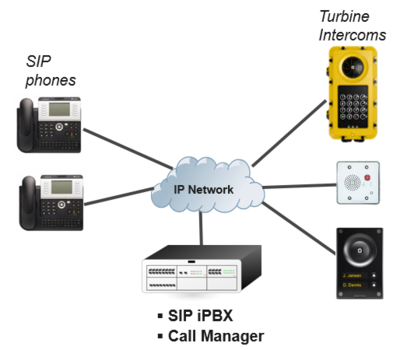
Turbine and INCA stations can be configured to operate in SIP Mode, and can be used with any SIP based iPBX or Call Manager.
The stations are easy to install and configure. They can be configured using a standard web browser (like Firefox or Chrome), or one can use the dedicated Intercom Management Tool IMT. This article describes configuration using the Web interface.
Contents
- 1 Getting Started
- 2 The station web interface
- 2.1 Station Main
- 2.2 SIP Configuration
- 2.2.1 SIP Settings
- 2.2.2 Audio Settings
- 2.2.3 Direct Access Key & Ringlist Settings
- 2.2.4 Relay/Output Settings
- 2.2.5 Time Settings
- 2.2.6 I/O Settings
- 2.2.7 Frontboard Mapping [Turbine only]
- 2.2.8 RTSP and ONVIF (Non video intercoms)
- 2.2.9 Video Settings
- 2.2.10 Advanced Video Settings
- 2.2.11 Scripts [Turbine only]
- 2.2.12 Audio Messages [Turbine only]
- 2.2.13 Multicast Paging
- 2.3 Station Administration
- 2.4 Advanced SIP
- 2.5 Advanced Network Settings
Getting Started
Main steps to get the station registered to a SIP server:
- Log on to the station
- Main Settings: Go to Station Main > Main Settings and set "Station Mode" = Use SIP, and enter the IP Settings.
- Account Settings: Select SIP Configuration > SIP Settings and enter as a minimum Display Name, Directory Number, Server Domain and Authentication User Name.
- Call Buttons (DAK keys): Select SIP Configuration > Direct Access Key Settings.
- OLED Labels: How to configure the OLED display used for labeling the call buttons in the station models TCIV-5+, TCIS-4 and TCIS-5
- Address Book: How to configure and maintain the Address Book used in the station models TCIV-6+, TCIS-6 and TCIV-6
The station web interface
Station Main
- Station Information page shows current status and information about the station, suuch as firmware version and IP Address
- Main Settings: Here the mode of operation is set, the network settings, and the model type.
SIP Configuration
SIP Settings
- Account Settings: Configure relevnt parameters for the SIP account
- Call Settings: A number of Call related parameters are available
Audio Settings
Audio Settings: A number of Audio related parameters are available
Direct Access Key & Ringlist Settings
- Direct Access Keys (DAK) are the Call Buttons or speed-dial buttons you find on most intercom stations.
- Ring List is used to configure Call Escalation (i.e. forwarding of unattended calls), and for Parallel Ringing.
To configure Call Buttons and Ring List, see Direct Access Key & Ringlist Settings (SIP)
Relay/Output Settings
All IP Intercom stations (execpt the desktop models) have a built-in relay which can be used for door opening, call indication lamp etc. The relay can be controlled by a DTMF digit, or by a number of different call events and station statuses.
For details about relay configuration, see Relay Settings
Time Settings
The user is able to configure time by either enabling NTP and specifying NTP server, or setting up time manually. On Master stations with display the configured time is shown on display.
See Time Settings for details.
I/O Settings
The Turbine stations have 6 I/O's which can be used as Inputs or Outputs. By default all I/O's are set as Inputs.
For details about configuration of inputs and outputs, see I/O Settings.
Frontboard Mapping [Turbine only]
When making customized stations based on the Turbine Frontboard, it is possible from the station web interface to define DAK actions and LED behavior. This is supported when front board type is set to TCIS 1/2/3 and TCIV 1/2/3, and the station operates in Pulse or SIP mode.
For more details, see Button and LED configuration for customized stations (SIP)
RTSP and ONVIF (Non video intercoms)
RTSP Settings: see RTSP Settings for Non-Video Intercoms
ONVIF Settings: see ONVIF Settings for Non-Video Intercoms
Video Settings
See article Video Settings on how to set parameters for the camera and stream options.
Advanced Video Settings
RTSP Settings: see RTSP Settings for Video Intercoms
ONVIF Settings: see ONVIF Settings for Video Intercoms
Scripts [Turbine only]
Scripts (Virtual I/O) is a feature for activating scripts on station events. The supported script languages are Lua and other shell scripting languages. This can be used for example to execute scripts towards other systems, e.g. access control systems, triggered by a DTMF digit. These scripts can be uploaded and configured via the menu options:
- Script Upload
- Script Configuration
- Script Events
The Scripting feature is supported on Turbine stations only.
For more details, see Virtual I/O
Audio Messages [Turbine only]
Prerecorded audio files can be uploaded to a Turbine IP Station, and the audio messages can be triggered by various events occuring on the station. The audio message files are uploaded from the station webinterface or from the VS-IMT tool.
See Audio Messaging for more details.
Multicast Paging
Multicast Paging enables IP intercom stations in SIP mode to receive VoIP audio as multicast paging from 3rd party iPBX (e.g. Asterisk). The feature is supported by both INCA stations and Turbine stations. Up to 10 different Multicast paging groups can be defined.
See Multicast Paging (SIP) for details.
Station Administration
Logging
Logs can be useful for debugging and troubleshooting purposes. See Logging - IP Stations on how to enable and collect logs.
Change Password
The password for web access and for accessing the display setup menus can be changed, see Password (IP Stations).
Backup and Restore
From the web interface of the station it is possible to backup and restore the configuration data. See Backup and Restore for more information.
Manual Upgrade
The software in the stations can be upgraded via the web interface of the station. The procedure is slighty different depending on the type of station:
Language Settings [INCA only]
In the INCA type stations it is possible to change the language of the display texts. This does not affect the texts in the web server interface. See Language Settings for details.
Keyboard [INCA only]
On the INCA Stations there is an option to set Keyboard Type. This is typically used for the IP Substation kit or the IP Master kit when building customized stations. See Keyboard Settings for further details.
Advanced SIP
Updates (TFTP Provisioning)
IP stations may be set up to automatically poll configuration from a TFTP server. The IP address of this TFTP server can be obtained using DHCP procedures or be manually configured. See TFTP Provisioning for more information.
Tone test
The tone test is designed to check whether the microphone and loudspeaker is working by playing a tone and detecting the sound pressure level. If the sound pressure level is below a chosen threshold the test fails. The result of the tone test is reported using SNMP traps, which must be turned on in the SNMP configuration.
For configuration of the Tone test, see Tone Test (IP Stations)
Web Call
Webcall makes it possible to establish a call directly from the station web. See Web Call for more information.
Advanced Network Settings
SNMP
A set of SNMP functions are available in the IP station. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol for centralizing the management of devices in IP networks.
See SNMP in IP Stations for futher information.
802.1X
IEEE 802.1X is an IEEE Standard for port-based Network Access Control (PNAC). It provides an authentication mechanism to devices wishing to attach to a LAN, either establishing a point-to-point connection or preventing it if authentication fails. For details on configuration, see IEEE 802.1X.
Firewall
All IP Stations have an embedded firewall. See Firewall for details.
VLAN Tagging [INCA, IPDM and IPDMH only]
VLAN Tagging is the practice of inserting a VLAN ID into a packet header in order to identify which VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) the packet belongs to. More specifically, switches use the VLAN ID to determine which port(s), or interface(s), to send a broadcast packet to.
For details on configuration, see VLAN Tagging (IEEE 802.1Q).